Introduction

(A graphic we put together to illustrate different projects, companies, and people who have been influential in the crypto space, by no means is this a complete depiction as the crypto space is huge and new projects are constantly appearing).
Ever since the inception of BitCoin back in 2008 the interest and overall development around Cryptocurrency technology and the underlying Blockchain has grown considerably with many large companies and services emerging.
This page on our glossary aims to summarise and provide a breakdown of key companies, influential figures, and platforms that have contributed to the Crypto or “web3” ecosystem as it stands today.
Crypto exchanges

CoinBase

Coinbase Global, Inc. is a publicly traded corporation in the United States that provides a Bitcoin exchange platform. It is the largest cryptocurrency exchange by trading volume in the United States, and it is a distributed firm with all staff working remotely. Brian Armstrong and Fred Ehrsam created Coinbase in 2012 after receiving a $150,000 funding infusion from the Y Combinator startup accelerator program.
Following Armstrong’s Reddit posts, Fred Ehrsam, a former Goldman Sachs trader, joined as a co-founder. Ben Reeves, a British programmer and co-founder of Blockchain.info, broke ways with Armstrong soon before the Y Combinator fundraising event. Coinbase was called after Coinbase transactions, which are used to add Bitcoin into proof of work cryptocurrencies.
If you want to trade cryptocurrencies, you can also read our post on the best cryptocurrency exchanges for Australians, best Cryptocurrency exchanges for Taiwan end-users , top Singapore Crypto trading apps as well as for different markets such as New Zealand, Norway, Hong Kong and Dubai. These platforms are ideal for beginners as well as advanced users looking to conduct spot trading or margin trading.
The startup offered services to buy and sell bitcoins via bank transfers in October 2012. Union Square Ventures made a $5 million Series A investment in the company in May 2013, followed by a $25 million investment in December. In the same year, Olaf Carlson-Wee was hired as the company’s first employee.
In 2014, the company bought Blockr and Kippt, gained insurance, and introduced a vault system for secure Bitcoin storage. To accept Bitcoin payments, the company worked with Overstock, Dell, Expedia, Dish Network, and Time Inc. in 2014. Coinbase became a subsidiary of Coinbase Global in April 2014.
Coinbase offers a variety of cryptocurrency solutions to retail and institutional investors, such as Coinbase Pro, Coinbase Wallet, Coinbase Prime, Coinbase Custody, USD Coin, Coinbase Card, and Coinbase Earn. These products allow users to buy, store, and trade multiple cryptocurrencies, as well as use a DApp browser to access decentralized crypto programs.
Coinbase Prime and Coinbase Custody are offered for institutional traders. USD Coin, a digital stablecoin that allows customers to exchange US dollars for faster-trading currencies, Coinbase Card, and Coinbase Earn, a cryptocurrency learning platform that rewards users with small amounts of altcoins for watching videos and taking quizzes, are among the other cryptocurrency-related products.
Coinbase also creates an API for developers and merchants to use in order to build applications and accept digital currency payments.
In September of 2022 Blackrock, the world’s largest investment manager teamed up with CoinBase in a major deal enabling their clients to add Cryptocurrencies to their asset portfolios.
Binance

Binance Holdings Ltd, which was created in 2017, manages the world’s largest cryptocurrency exchange in terms of daily trading volume at the time of publishing. In 2021, it was being investigated by the US and UK for money laundering and tax evasion.
Binance has released two cryptocurrencies that it created: Binance Coin (BNB) and BinanceUSD (BUSD). BNB debuted in July 2017 as an Ethereum token before transitioning to Binance Smart Chain (BSC), which debuted in September 2020. BSC was later merged with the older Binance Chain and relaunched as the BNB chain. BNB Chain employs “Proof of Stake Authority,” a hybrid of proof of stake and proof of authority. It has 21 validators who have been approved. Binance Coin was the cryptocurrency with the third-greatest market capitalization as of 2021. Binance allows its users to pay fees for BNB exchanges.
BNB Chain is compatible with the Ethereum virtual machine (EVM) and supports smart contracts. There have been numerous criticisms of the Binance Smart Chain and its level of centralization. Binance was ordered by the UK Financial Conduct Authority to cease regulated activities in June 2021.
Fusion Solutions, created in 2005 in Shanghai by CEO Changpeng Zhao, developed high-frequency trading solutions for stockbrokers. As the third member of the Blockchain.info team, he joined the company in 2013. He also spent less than a year as CTO at OKCoin, a platform for spot trading between fiat and digital assets. He was hired in this job in 2014 by Yi He, with whom he eventually co-founded Binance.
The company was created in China in 2017, however, it relocated its servers and headquarters out of the country before the Chinese government banned cryptocurrency trading in September 2017. Zhao approached Binance and assisted in rewriting parts of the white paper for Binance’s $15 million ICO.
Gemini

Gemini Trust Company, LLC is a cryptocurrency exchange and custodian in the United States that allows users to purchase, sell, and store digital assets. Cameron and Tyler Winklevoss founded the company in 2014, and it now operates in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, South Korea, Hong Kong, and Singapore.
Gemini started allowing Bitcoin purchase and storage using a complicated system of private keys and password-protected environments. The New York Department of Financial Services granted Gemini a Limited Purpose Trust Charter in October 2015. Gemini has expanded its financial offerings, which now include FIX and API support.
Governor Andrew Cuomo approved Gemini as the first licensed Ethereum exchange in the United States in 2016. In 2017, Gemini enabled customers to withdraw Ethereum Classic (ETC) and Bitcoin Cash.
The Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) used Gemini to settle Bitcoin futures contracts in December 2017, utilizing its dollar-denominated auction price. CBOE stopped listing Bitcoin futures in March 2019. In April 2018, Gemini launched Block Trading, letting users purchase and sell digital assets outside of its order books.
Gemini approved Zcash (ZEC) trading and custody services in May 2018, and in September 2018, Gemini released the Gemini dollar (GUSD), a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar one-to-one. Gemini got digital asset insurance for tokens and cryptocurrencies held on its exchange in October 2018.
Gemini launched Block Trading in April 2018, allowing customers to purchase and sell massive volumes of digital assets outside of its continuous order books. The platform also made use of NASDAQ’s SMARTS technology to monitor trades and combat fraud. In May 2018, the New York Department of Financial Services permitted Gemini to offer Zcash (ZEC) trading and custody services on its platform, making it the first licensed exchange to do so.
Gemini has got regulatory permission for the Gemini dollar (GUSD) currency, a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar one-to-one. Gemini got digital asset insurance covering tokens and coins held on its exchange in October 2018, arranged by Aon and underwritten by a consortium of worldwide underwriters.
Gemini Trust Co. purchased Nifty Gateway, an NFT platform, in November 2019 with the intention of becoming a custodian for diverse assets. Cooperation with Samsung was announced in May 2020, allowing Samsung smartphone users to link their Samsung Blockchain Wallets to their Gemini accounts to monitor balances and transfer cryptocurrency.
Gemini raised $400 million in November 2021, valuing the New York parent firm, Gemini Space Station, LLC, at $7.1 billion.
The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) sued Gemini on June 2, 2022, for claimed misrepresentation of the company’s exchange and futures contracts during 2017 discussions with the CFTC. In addition to monetary penalties, the suit seeks to prevent Gemini and its affiliates from trading commodities and receiving additional investments.
Cameron and Tyler Winklevoss also announced on June 2 that they will be laying off 10% of the company’s employees, citing a “contraction phase” known as “crypto winter” in the cryptocurrency business.
Etoro

eToro, founded in 2007, is a social trading and multi-asset investment company specializing in financial services. Founded in 2007, the company has raised over $162 million in funding. Its eToro OpenBook platform, CopyTrader feature, and Android app have been popular among investors. In 2013, eToro introduced stocks, CFDs, commodities, and currencies, and in 2014, cryptocurrencies were added to its investment instruments.
Firmo, a Danish blockchain business, was purchased by eToro in 2019 for an unknown value. The business unveiled a sentiment-based crypto portfolio in October 2019 that analyzes Twitter’s opinions of digital assets on a favorable or negative basis. The company bought Delta, a provider of a cryptocurrency portfolio tracking application, in November 2019. The eToro cryptocurrency trading platform and standalone cryptocurrency wallet were made available to US customers in March 2019. The firm claimed to have 20 million subscribers and to operate in 140 countries in 2021.
Through a reverse subsidiary merger with FinTech Acquisition Corp V, supported by former Bancorp CEO Betsy Z. Cohen, eToro announced plans to go public in March 2021. The combined business will be known as eToro Group Ltd, and its indicated enterprise value at closure will be $10.4 billion. Marq Millions, the UK business of e-money, which was rebranded eToro Money, was bought by the company in 2020. The business introduced the eToro Money debit card for UK citizens in December 2021.
Kraken

Jesse Powell, Thanh Luu, and Michael Gronager launched Kraken, a cryptocurrency exchange based in the United States, in 2011. It was valued at $10.8 billion and was one of the first Bitcoin exchanges to be listed on Bloomberg Terminal. Since 2018, Kraken has faced regulatory inquiries and has agreed to pay over $30 million in fines to settle disputes. It obtained a $5 million Series A investment in 2014 and was chosen to help with the investigation into Mt. Gox’s stolen bitcoins.
Coinsetter was bought by Kraken in 2016, CleverCoin in 2017, and Cryptowatch in 2017. Every day, the company adds up to 50,000 new users. Due to escalating costs, it ceased operations in Japan in 2018. It purchased Crypto Facilities in 2019 and raised $13.5 million from 2,263 investors in June 2019.
Kraken was given a special purpose depository institution (SPDI) charter in Wyoming in September 2020, making it the first cryptocurrency exchange in the United States. Kraken sought further funding in early 2021 at a valuation of more than $20 billion, with Tribe Capital becoming the company’s second-largest institutional investor.
Crypto.com

Crypto.com is a Singapore-based cryptocurrency exchange. According to reports, the corporation has 50 million clients and 4,000 staff as of May 2022. Cronos (CRO) is the exchange’s own exchange token.
Crypto.com, which was launched in Hong Kong in 2016, was renamed Crypto.com in 2018 after purchasing a domain owned by cryptography expert Matt Blaze for $5-10 million. Foris DAX Asia, a Singapore-based subsidiary of Foris DAX MT (Malta) Limited, operates the company.
Crypto.com had over 50 million active users as of May 2022. A hack totaling $15 million in stolen Ether halted withdrawals in January 2022, however, withdrawal services were restored. Crypto.com cut off hundreds of staff, and their token, Cronos, lost about $1 billion in value in November 2022 owing to concerns over FTX’s demise. CEO Marszalek informed users that the exchange was operational.
Crypto.com offers an app, exchange, wallet, and NFT marketplace. They teamed with Shopify in May 2022 to let businesses who use the e-commerce platform accept cryptocurrency payments.
Digital Asset Holdings

Sunil Hirani, Don R. Wilson, Yuval Rooz, Shaul Kfir, and Eric Saraniecki co-founded Digital Asset (or Digital Asset Holdings, LLC) in 2014. It creates products for banks and other financial institutions based on distributed ledger technology (DLT).
The Wall Street Journal’s Moneybeat blog noted on June 25, 2015, that the “acquisition of HyperLedger might raise eyebrows in the Bitcoin community, where there is an aversion to the idea that Wall Street might co-opt blockchain technology and strip it of its decentralized nature”.
Cryptocurrencies

Below is a brief summary of some of the many Cryptocurrencies out there:
BitCoin (The first Cryptocurrency)

BitCoin was the first Cryptocurrency and Blockchain platform built to be a decentralized currency and makes use of a public and permanent ledger to record transactions over the peer-to-peer network.
Satoshi Nakamoto created the cryptocurrency known as Bitcoin in 2008; it utilizes cryptography to authenticate transactions and store them in a blockchain. As of November 2021, nine nations explicitly forbade the usage of Bitcoin, and another 42 did it implicitly. Some governments have utilized Bitcoin in some way, like Iran utilizing it to get around sanctions, El Salvador using it as legal tender, and Ukraine taking cryptocurrency donations to fend against the Russian invasion.
However, in 2018, Nobel Prize winners criticized Bitcoin as an economic bubble. Bitcoin mining uses a proof-of-work technique that is computationally challenging, uses a lot of electricity, and is said to contribute towards climate change. Around 200 million tonnes of carbon dioxide have been released since Bitcoin’s introduction, or 0.04% of total carbon dioxide since 2009.
Satoshi Nakamoto created Bitcoin in 2008 as a cryptocurrency that employs encryption to authenticate transactions and record them in a blockchain. As of November 2021, nine countries had explicitly prohibited the usage of Bitcoin, while 42 had impliedly prohibited it. Some nations have made Bitcoin legal tender, and Ukraine and Iran have used it to circumvent sanctions.
However, Nobel Prize winners in 2018 denounced Bitcoin as an economic bubble. The Bitcoin mining proof-of-work process is computationally challenging, consuming growing amounts of electricity and contributing to climate change. Bitcoin has emitted around 200 million tonnes of CO2 since its inception, accounting for approximately 0.04% of total CO2 emissions since 2009.
Bitcoin has gained much popularity and notoriety over the years as it was very much the poster child for Cryptocurrencies and has received mainstream recognition across the world.
Litecoin

Litecoin (LTC; sign: ) is a peer-to-peer cryptocurrency and open-source software project released under the MIT/X11 license. Litecoin, which was inspired by Bitcoin, was one of the first altcoins to emerge, debuting in October 2011. Technically, the Litecoin main chain is based on a slightly modified version of the Bitcoin software which is known as a fork.
Lower transaction fees, faster transaction confirmations, and faster mining difficulty retargeting are the practical impacts of coding variations.
Because of its fundamental similarities to Bitcoin, Litecoin has been dubbed the “silver to Bitcoin’s gold.” In 2022, Litecoin soft-forked to introduce optional privacy capabilities via the MWEB (MimbleWimble extended block) update.
How it differs from BitCoin:
Litecoin is a cryptocurrency with a block time target of 2.5 minutes, which is four times faster than Bitcoin’s 10 minutes. It employs the scrypt algorithm, which consumes more memory and is more difficult to design and implement than Bitcoin’s SHA-256 algorithm.
Litecoin and Dogecoin are also mined together, enhancing miner remuneration and network security. It has an 84,000,000 maximum circulating supply, which is four times greater than Bitcoin’s 21,000,000. Both Litecoin and Bitcoin retarget their mining difficulty every 2016 block, but due to Litecoin’s 4x quicker block speed, retargeting occurs every 3.5 days, compared to 14 days for Bitcoin.
In May 2022, a soft fork added MWEB optional privacy to Litecoin’s basic layer, allowing private amounts maintained within wallets and transaction amounts within MWEB.
Point-of-sale infrastructure for Litecoin is provided by third-party suppliers such as Verifone, BitPay, and Coingate, with Litecoin accounting for less than 3% of BitPay transactions but presently accounting for 21% of BitPay transactions by payment count.
USDCoin

USD Coin (USDC) is a digital stablecoin that is tied to the US dollar. USD Coin is controlled by the Centre consortium, which was created by Circle and comprises members from the cryptocurrency exchange Coinbase and Bitmain, a Circle investor. USDC is a private company that is not to be mistaken with a central bank digital currency (CBDC).
Tether

Tether, a cryptocurrency stablecoin backed by assets, was created in 2014 by Tether Limited Inc., which is owned by Hong Kong-based iFinex Inc., which also owns Bitfinex. Tether has produced the USDT stablecoin on eleven protocols and blockchains as of July 2022.
Tether Limited, which was originally supposed to be worth $1, keeps $1 in asset reserves for every USD 1 issued. It is the largest stablecoin in terms of trading volume and market capitalization, accounting for 64% of the market and ranking among the most traded cryptocurrencies worldwide. Tether surpassed Bitcoin to become one of the world’s most-traded cryptocurrencies in 2019.
Ethereum
![]()
Ethereum is a global network of computers that obey a set of rules known as the Ethereum protocol. The Ethereum network serves as the foundation for communities, applications, organizations, and digital assets that anyone may create and utilize. You may open an Ethereum account from anywhere, at any time, and explore a multitude of apps or develop your own.
Ethereum’s decentralized structure empowers individuals and communities to engage in innovative endeavors, from creating decentralized applications (dApps) that revolutionize industries to participating in decentralized governance through entities like Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs). At the heart of this ecosystem is Ether (ETH), Ethereum’s native cryptocurrency, which serves both as a means of exchange and a vital element for securing the network.
Ethereum 2.0 will use a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, aiming to enhance scalability and energy efficiency. Users will be able to stake their ETH and participate in network validation as a result of this development, opening the path for a more sustainable and accessible worldwide platform. Ethereum’s blockchain also makes it easier to create and manage digital assets, culminating in a world of tokens and non-fungible tokens (NFTs), which enable new forms of digital ownership. Ethereum faces obstacles such as network congestion and scalability as it expands, however developing layer 2 scaling solutions are tackling these issues. Transaction confidentiality is also being improved through privacy technologies such as zk-SNARKs and Ring Signatures.
Ethereum is a decentralized network of connected computers, known as nodes, that run software that adheres to the Ethereum protocol. Nodes can be run by anyone, however to secure the network, ETH (Ethereum’s native token) must be staked. The Ethereum source code is not produced by a single body, and numerous implementations in various programming languages are produced by independent groups, promoting community contributions.
Ripple

Ripple is a real-time gross settlement system, currency exchange, and remittance network developed by Ripple Labs Inc., a technology company based in the United States. It supports tokens representing fiat cash, cryptocurrencies, commodities, or other units of value, and was released in 2012. Ripple wants to make worldwide financial transactions secure, quick, and nearly free, with no chargebacks. The SEC sued Ripple Labs and its executives in December 2020 for selling unregistered XRP tokens. The court ruled in July 2023 that XRP is not a contract.
Jed McCaleb, Arthur Britto, and David Schwartz founded Ripple, a blockchain-based payment system. Ryan Fugger, who previously created OpenCoin and XRP, a digital currency for financial institutions, created it. Over 100 banks had signed up by 2018, however the majority employed Ripple’s XCurrent messaging system. According to the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT), Ripple and other blockchain solutions are limited to bilateral and intra-bank applications because to unresolved scaling difficulties. Ripple is based on a shared ledger, which is a distributed database that stores information about all Ripple accounts. Independent servers operate the network, which might belong to anyone, including banks or market makers. Payments are irreversible and cannot be reversed. Ripple Labs provided code for consensus verification.
Dogecoin

Dogecoin is a cryptocurrency designed as a joke by software programmers Billy Markus and Jackson Palmer to satirise the rampant cryptocurrency speculation of the time. It is regarded as the first “meme coin” as well as the first “dog coin.” Dogecoin’s emblem and namesake is the Shiba Inu dog from the “doge” meme. It was launched in December 2013 and swiftly grew its own online community before reaching a peak market valuation of more than US$85 billion on May 5, 2021. It is the sleeve sponsor of Watford Football Club as of 2021. Dogecoin.com describes the money as a “fun and friendly Internet currency” and was developed with the assistance of Reddit. Dogecoin’s market value surpassed $8 million thanks to a dedicated blog and forum, making it the seventh biggest cryptocurrency globally at the time. These types of coins are usually referred to as memecoins and made for comedic value however some people call them “shitcoins” due to them having no real underlying value or utility.
Stellar Lumens

Stellar, also known as Stellar Lumens, is an open-source, decentralized system for low-cost digital currency to fiat money transfers that enables cross-border transactions between any two currencies.The Stellar protocol is backed by the Stellar Development Foundation, a Delaware charitable corporation, however it does not have IRS 501(c)(3) tax-exempt status.Stellar, a decentralised payment network and protocol with a native currency, Stellar, was founded in 2014 by Jed McCaleb and Joyce Kim. The nonprofit Stellar Development Foundation was founded with $3 million in startup investment from Stripe CEO Patrick Collison. At the time of its introduction, the network had 100 billion stellars, with 25% going to non-profits. Stellar has 3 million registered user accounts and a market valuation of about $15 million by 2015. Lightyear.io was formed as the commercial arm in 2017, and Interstellar was acquired by Lightyear Corporation in 2018.
Blockchains

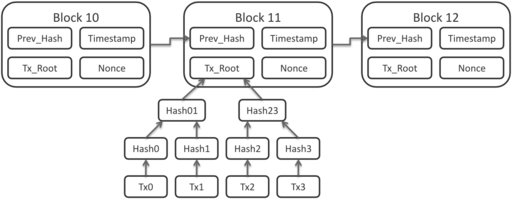
A blockchain is similar to a digital ledger in that it securely and irreversibly records transactions and information. Consider it a chain of connected blocks, each containing data. Once data is entered into a block, it is locked and linked to the previous one, forming a chain, making it extremely difficult for anybody to alter or tamper with the information, making it a trusted and transparent system for a variety of applications, including cryptocurrencies like as Bitcoin.
There are various Blockchains out there and each Cryptocurrency relies on one to work, many “altcoins” will leverage an existing Blockchain (usually the 2 biggest which are the ETH and Bitcoin chains) however there are alternative chains that are used by some Cryptocurrencies as well as decentralized apps and projects.
Here are some other well known chains outside the oldest which is the Bitcoin blockchain:
ETH Chain
Ethereum, a decentralized blockchain with smart contract capability, is the second most valuable cryptocurrency behind bitcoin. It was founded in 2013 and allows customers to deploy permanent, immutable applications without the usage of intermediaries such as brokerages or banks. It also allows for the creation and trade of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) linked to certain digital assets. Many other cryptocurrencies use Ethereum to conduct Initial Coin Offerings. It switched its consensus technique from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake in September 2022, cutting its energy usage by 99% which was criticized by many in the Crypto community who believed a traditional Proof Of Work method was better much like the traditional Bitcoin chain.
Microsoft, IBM, JPMorgan Chase, Deloitte, R3, Innovate UK, Barclays, UBS, Credit Suisse, Amazon, Visa and other enterprise companies are testing Ethereum-based software and networks independently of the public Ethereum chain for their own use cases.
There a a number of differeing use-cases the ETH chain is been used for such as helping with settlement of international transactions and creating smart contracts as well as other things like:
- Permissioned ledgers: Permissioned ledgers are similar to private digital notebooks in which only trusted players, such as banks or authorized persons, can view and write transactions. They protect users’ privacy and security while allowing authorized users to collaborate and collect data in a regulated and visible manner.
- NFTs: These are unique digital items that are represented by unique digital identifiers and can include artwork, collectables and other digital assets that can be bought and sold.
- DeFi: The ETH chain is home to many different types of DeFi (Decentralized Finance) applications that have a wide range of different financial features for different uses.
Solana Chain

Solana is a blockchain platform developed by Solana Labs, which was created by Anatoly Yakovenko and Raj Gokal in 2020. For smart contract functionality, it employs a proof-of-stake system, and its native cryptocurrency is SOL. Solana’s market cap was $55 billion in January 2022, despite outages, hacks, and class action lawsuits. However, following FTX’s bankruptcy, it plummeted to roughly $3 billion before rising to $7 billion in 2023.
In March 2020, Solana, a blockchain optimized for smart contracts and decentralized apps, was introduced. Large transactions, on the other hand, have resulted in disruptions. Solana Labs sold $314 million of its native cryptocurrency, SOL, to Andreessen Horowitz and Polychain Capital in June 2021. In July 2022, Solana was accused of distributing unregistered securities tokens and misled investors about the entire circulating quantity in a class action complaint. In August 2022, 9,231 Solana wallets were hacked, resulting in a loss of $8 million. The SEC sued Coinbase in June 2023, saying that it failed the Howey Test and hence qualified as a security.
Individuals

Like the technology frameworks there are many key people involved in different companies throughout the Crypto and Blockchain sector, here are a few names of some of the people involved in the space and companies they founded or are involved with.
Vitalik Buterin (Co-founder of Ethereum)
Vitaly Dmitrievich Buterin (Russian: итали митpиеви утерин), also known as Vitalik Buterin (Russian: италик утерин, born 31 January[2] 1994), is a Russian-Canadian computer programmer and Ethereum co-founder. Buterin got interested in bitcoin early on, co-founding Bitcoin Magazine in 2011. Buterin and Gavin Wood, Charles Hoskinson, Anthony Di Iorio, and Joseph Lubin launched the Ethereum blockchain back in 2014 and today is one of the largest Cryptocurrencies and blockchains powering many different applications.
Buterin’s Ethereum is a decentralized mining network and software development platform that enables the development of new coins and apps that share a single blockchain. Ethereum, which was first detailed in a white paper in 2013, gained popularity in 2014 and was publicly revealed during the North American Bitcoin Conference in Miami. Buterin has worked on complex problems in computer science, economics, and philosophy, and he is grateful for the opportunity to engage in a multidisciplinary field. He is motivated to build decentralized money because his World of Warcraft character was nerfed by patch 3.1.0, causing him to resign.
Buterin, who was born in Russia in 1994, was a computer scientist with a special knack for numbers and numerical patterns. He went to Canada when he was six years old and became interested in mathematics, programming, and economics. At the age of 17, he heard about Bitcoin from his father, Dimitry Buterin. Buterin went to the University of Waterloo after high school, where he worked as a research assistant for Ian Goldberg, co-creator of Off-the-Record Messaging and Tor Project chairman. He got a bronze medal at the International Olympiad in Informatics in 2012. He proposed Ethereum in a white paper in 2013. In 2014, he dropped out of university and was given a $100,000 Thiel Fellowship. Buterin was awarded an honorary doctorate by the University of Basel in 2018.
Gavin Wood (Co-founder of Ethereum)
Gavin James Wood is a computer scientist from England who co-founded Ethereum and created Polkadot and Kusama. Wood was born in the English city of Lancaster. He was educated at Lancaster Royal Grammar School. He earned a Master of Engineering (MEng) in Computer Systems and Software Engineering from the University of York in 2002 and a PhD in 2005 with the title “Content-based visualisation to aid common navigation of musical audio.”
Wood, a former Microsoft research scientist, was a key architect of the Ethereum blockchain, which he described as “one computer for the entire planet.” He helped to create Solidity, a programming language for creating smart contracts, as well as the Ethereum Virtual Machine, the Ethereum runtime system for smart contracts. Wood left the Ethereum Foundation in 2016 after serving as its first chief technology officer. He launched Parity Technologies, which provides a client for the Ethereum network as well as tools for businesses that use blockchain technology. In 2018, Wood was the chief web officer of Parity. He also formed the Web3 Foundation, a non-profit organization dedicated to decentralized internet infrastructure and technologies, beginning with the Polkadot network which makes use of a proof of stake consensus method and also enables developers to create their own blockchain.
CZ (Changpeng Zhao)
Changpeng Zhao (Chinese: ; pinyin: Zhào Chángpéng), sometimes known as CZ, is a Canadian businessman, investor, and software developer of Chinese origin. Zhao is the co-founder and CEO of Binance, which as of July 2022 had the world’s largest cryptocurrency exchange by trading volume. According to the Bloomberg Billionaires Index, Zhao is the 136th richest person on the planet, with a net worth of $13.1 billion as of December 2022.
Binance, which started in July 2017, raised $15 million in its initial coin offering and in less than eight months became the world’s largest cryptocurrency exchange by trading volume. Binance Coin was launched in 2017, Binance Smart Chain in 2019, and Binance.US in 2019. Zhao was ranked third on Forbes’ list of “The Richest People in Cryptocurrency” in February 2018. Binance.US, Binance’s US affiliate, was launched in 2019. Binance withdrew its application to launch a Singapore-based cryptocurrency exchange in 2021. The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) launched a lawsuit against Binance and Zhao in March 2023, accusing them of wilful avoidance of US law and alleged violations of derivatives rules. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) of the United States filed a complaint against Zhao in June 2023 alleging violations of US securities rules.
Charlie Shrem
Charles Shrem IV (born November 25, 1989) is a bitcoin supporter and entrepreneur from the United States. He was a founding member of the Bitcoin Foundation and co-founded the now-defunct startup company BitInstant which was one of the most early Cryptocurrency exchange platforms. He was sentenced to two years in prison in 2014 for assisting and abetting the operation of an unauthorized money-transfer firm associated with the Silk Road underground marketplace.In 2016, he was released from prison. He joined Jaxx as chief operational officer in 2017 and created bitcoin adviser CryptoIQ.
Shrem, a college senior, began investing in bitcoin in 2011 after the site crashed and he lost his bitcoins. He and Gwen Nelson co-founded BitInstant, an easy-to-use startup that charged a fee for bitcoin purchases at over 700,000 locations. The company expanded and was funded by angel investor Roger Ver and Winklevoss Capital Management. BitInstant handled 30% of all bitcoin transactions by 2013. Shrem is a Bitcoin purist and a member of the Bitcoin Foundation’s founding board. He has spoken at bitcoin industry events and co-owned Manhattan bar EVR, the city’s first to accept bitcoin as payment.
Conclusion
We hope you found this page to be helpful and learn more about some of the key companies, people and technologies in the Crypto space. Be sure to check out our blog for more as well as business services.
Related content from our website:
How to get started buying Bitcoin in Australia
Digital Wallets / Smart Wallets
What is a Neobank and how does it work?
Fintech (Financial Technology)
What are some of the best Cryptocurrencies to buy based on up-to-date prices?
How can you accept Cryptocurrency payments on your website?
Blockchain Explorer Definition
Cryptocurrency Market Analysis Definition
What are Initial Exchange Offerings (IEOs)
Some of the best small business loan providers in Australia
Some of the most top-rated CFD trading platforms/brokers for Dubai users in the UAE
Net worth calculator – online tool
Mortgage affordability calculator – online tool
Curated summary of the best CFD brokers/apps in Australia
Leading Cryptocurrency exchanges for Indian users
Top-rated Crypto exchanges for South Africa
Some of the best Cryptocurrency exchanges & apps for Saudi Arabia
Some of the best small business loan providers for Perth
CMC Markets Alternatives for Australia
Coinspot alternatives platforms Australian Crypto users
Cryptocurrency wallet data recovery services by AGR Technology
Web3 Marketing Services By AGR Technology
Some of the best loan providers for Melbourne businesses
The best day trading applications/platforms for Australians
Top Forex trading brokers for Canadian users
Top Etoro alternatives for Australian forex traders
What to look for when choosing a neobank app
Some of the leading forex trading platforms for New Zealand users
Top Sydney business loan brokers
Top Alternatives to Swyftx for Australian Crypto users
Top-rated Alternatives to Etoro for Australian CFD traders
Some of the best Cryptocurrency exchanges/apps for Canadians
Web3 Software Development Services
NFT Digital Marketing Services
(Guide) How to buy Cryptocurrency in Australia
Best places to earn interest on your Cryptocurrency assets
How to buy Bitcoin online or other Cryptos
What is Web3 Gaming?
Best stock market trading platforms Australia to buy shares
How to pay overseas contractors from Australia online
How to buy Etherium (Eth) in Australia
Source(s) cited:
Coinbase. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coinbase. Published June 6, 2013. Accessed July 20, 2023.
(2017). Binance [Online]. Wikipedia. Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binance (Accessed: 20 July 2023).
“Gemini (company).” Wikipedia. January 8, 2016. Accessed July 20, 2023. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gemini_(company).
Kraken (company). Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kraken_(company). Published November 21, 2015. Accessed July 20, 2023.
“eToro” Wikipedia, 17 June 2009, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EToro. Accessed 20 July 2023.
“Digital Asset Holdings.” Wikipedia. September 29, 2015. Accessed July 20, 2023. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_Asset_Holdings.
Digital Asset Holdings LLC, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Jessel, Ben. “Digital Asset Steps Up A Gear In Enterprise Blockchain” 19 Feb. 2020, www.forbes.com/sites/benjessel/2020/02/19/digital-asset-steps-up-a-gear-in-enterprise-blockchain/. Accessed 20 July 2023.
www.wsj.com/articles/BL-MBB-38507. Accessed 20 July 2023.
Liao, R. New York-based Digital Asset to help Japan’s financial giant SBI develop ‘smart yen’. https://web.archive.org/web/20220701042413/https://techcrunch.com/2022/05/31/japan-sbi-digital-asset-daml/. Published May 31, 2022. Accessed July 20, 2023.
“Crypto.com”, Wikipedia. 17-Nov.-2021. [Online]. Available: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Crypto.com. [Accessed: 21-July-2023].
“CO2 emissions – Global Energy Review 2021 – Analysis – IEA” www.iea.org/reports/global-energy-review-2021/co2-emissions. Accessed 21 July 2023.
Matthäus Wander, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
(2018). [Online]. Available at: https://f.hubspotusercontent30.net/hubfs/9304636/PDF/centre-whitepaper.pdf (Accessed: 21 July 2023).
(2009). Bitcoin [Online]. Wikipedia. Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bitcoin (Accessed: 21 July 2023).
Litecoin, Wikipedia (Oct. 20, 2012), https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Litecoin.
“USD Coin.” Wikipedia. April 7, 2020. Accessed July 21, 2023. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/USD_Coin.
Tether (cryptocurrency). Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tether_(cryptocurrency). Published December 5, 2017. Accessed July 21, 2023.
“Tether USDt Price | USDT Price Index, Live Chart and USD Converter” Binance, 22 Feb. 2023, www.binance.com/en/price/tether. Accessed 21 July 2023.
What is Ethereum?. Ethereum.Org. https://ethereum.org/en/what-is-ethereum/. Accessed September 29, 2023.
E. Rasure, (2023). Ripple Definition [Online]. Available at: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/r/ripple-cryptocurrency.asp (Accessed: 29 September 2023).
Fastcompany.Com [Online]. Available at: https://www.fastcompany.com/2682032/bitcoin-20-can-ripple-make-digital-currency-mainstream (Accessed: 29 September 2023).
Accessed September 29, 2023. https://github.com/dogecoin/dogecoin/blob/master/share/pixmaps/dogecoin256.png.
Dogecoin. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dogecoin. Published December 14, 2013. Accessed September 29, 2023.
Stellar (payment network), Wikipedia (Sept. 4, 2014), https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stellar_(payment_network).
Ethereum Foundation, CC BY 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
“Solana (blockchain platform)” Wikipedia, 10 Sept. 2021, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solana_(blockchain_platform). Accessed 29 Sept. 2023.
John Phillips, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
“Vitalik Buterin”, Wikipedia. 24-Jan.-2014. [Online]. Available: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vitalik_Buterin. [Accessed: 29-Sept.-2023]
TechCrunch, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
“Gavin Wood” Wikipedia, 21 Nov. 2017, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gavin_Wood. Accessed 29 Sept. 2023.
Aevozer, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
“Changpeng Zhao.” Wikipedia. March 8, 2018. Accessed September 29, 2023. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Changpeng_Zhao.
Cshrem, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
(2013, July 12). Charlie Shrem. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Charlie_Shrem
![logo-new-23[1] logo-new-23[1]](https://agrtech.com.au/wp-content/uploads/elementor/thumbs/logo-new-231-qad2sqbr9f0wlvza81xod18hkirbk9apc0elfhpco4.png)




