Introduction – What is DeFi, what does it mean and how does it work?
Decentralized finance (abbreviated DeFi) provides financial instruments without the use of intermediaries such as brokerages, exchanges, or banks through the use of smart contracts on a blockchain. People can use DeFi platforms to lend or borrow money from others, speculate on asset price movements with derivatives, trade cryptocurrencies, insure against risks, and earn interest in savings accounts.
DeFi employs a layered architecture and modular building blocks. Some applications advertise high-interest rates but can be risky.
Relevant articles from our blog:
Some of the best Crypto exchanges that work in New Zealand
Best Crypto Platforms in Australia
Some of the best Crypto platforms for Dubai and the UAE
Curated list of our top picks for Crypto exchanges in Hong Kong
List of our top picks for Crypto platforms in Norway
Quality Crypto trading apps for Taiwan consumers
Buyers guide / Comparison of Cryptocurrency platforms for Singapore users
Centralized Finance Vs Decentralized Finance (DeFi) – How they differ

Centralized finance
Centralized finance refers to the traditional financial system which involves a central bank such as the Federal Reserve (USA) and Reserve Bank (Australia) which sets interest rates and manages the core currency and then banking institutions that provide financial services such as loans, credit cards, and online banking services to send/receive money.
Centralized finance goes through intermediaries that hold and manage the funds on your behalf and are typically traditional banks that have existed for centuries however can also include centralized Cryptocurrency exchanges like Coinbase which manage the underlying wallet for you.
Centralized platforms are mostly regulated and follow a procedure called “Know Your Customer” and require you to submit an ID in order to use the platform such as a driver’s license or passport along with a picture of your face to verify your identity. Other types of centralized platforms from central banks are also been tested and aim to have a mix between both systems with efficiencies of digital platforms but centrally controlled by a Government.
Pros:
- Customer support options with banks and central exchanges offering in most cases 24/7 customer support
- Options to recover information if it’s lost, reset passwords, etc if forgotten
- Regulated entities that ensure the providers are held to high standards
- Fewer chances of fraudulent activity and money laundering taking place
Cons:
- Can be slow to send money internationally or between different banks
- Time required for verification
- Can be harder for some people to access based on where they live, the situation of their country, or personal circumstances
- Not necessarily inter-operable with other systems
- Fees can vary quite differently from platform to platform
Decentralized finance
Decentralized finance platforms in contrast work on a peer-to-peer approach without a centralized company or institution.
DeFi platforms work on a Blockchain network such as Solana or Ethereum and are driven by “smart contracts” which are essentially computer algorithms that contain different rulesets for the specific application and are designed to run on their own and allow users to coordinate transactions between each other.
These smart contracts are made up of a variety of predefined conditions that, when met, cause events to occur within the application, also known as a DApp (decentralized application).
By being built on peer-to-peer concepts and individual users managing their own Crypto assets and wallets users don’t need to go through verification and can transact much faster in what can be described as a vending machine where the application provides functionality on an ad-hoc as-needed basis. An example of this might be an exchange to convert one Crypto coin to another type (e.g. Ethereum to Litecoin).
Pros:
- Allows for rapid development and expansion of decentralized applications that can provide a wide range of functionality and tools for end-users in the Crypto space
- Depending on the application it can work across different blockchains so cross-compatibility is achievable
- Provides fast access to financial services via the Blockchain with privacy features built-in
- A diverse range of trading and purchasing options
- Can provide financial functionality to end-users that may not have had access to traditional financial products and services
- You have full control and management of your keys and Crypto assets
Cons:
- Due to being decentralized traditional safeguards and trusted intermediaries aren’t present so users are on their own in terms of keeping their data safe
- Without “know your customer” protocols malicious activity and money laundering are much more likely to become an issue on decentralized platforms
- Some applications may be hard to use and not user-friendly for people getting started in the space
- Can be unreliable if the underlying blockchain or framework used has inherent instabilities or issues
- If you accidentally direct transactions to another cryptocurrency wallet, they will be lost and unrecoverable. Furthermore, if you lose your wallet, you will lose all of your Crypto assets which are in contrast to a traditional bank where you can get a new credit card or get some funds recovered in a hack or accidental transfer
Image to compare the 2 together
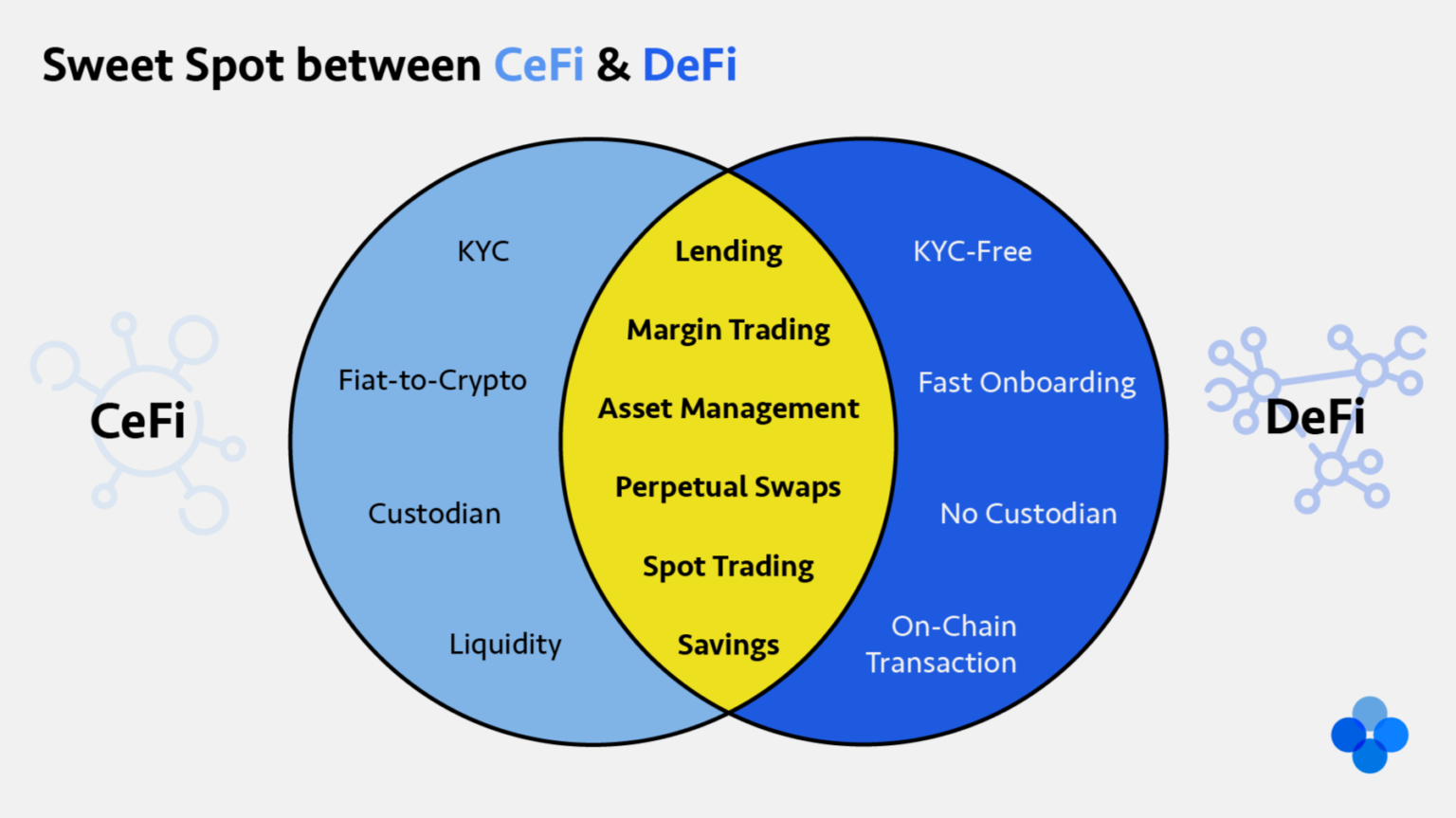
Image source: FiscalNepal
The history behind DeFi technology
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are innovative financial transaction protocols and alternative payment ecosystems that have arisen inside the decentralized finance framework. The multi-layered DeFi architecture or components, where each layer provides a specific function, are the foundation for CEXs, DEXs, and DEX aggregators.
In 2017, the Ethereum blockchain made smart contracts, the foundation of DeFi, widely accepted. Established in 2017, MakerDAO is a well-known lending DeFi platform specifically a DAO built on a stablecoin. In June 2020, Compound Finance began rewarding lenders and borrowers with cryptocurrencies.
As other sites imitated them, stacked investment opportunities known as “liquidity mining” or “yield farming” emerged. The Washington Post discussed decentralized finance strategies and associated concerns in July 2020.
Bloomberg reported in September 2020 that DeFi accounted for two-thirds of the cryptocurrency market in terms of price changes and that DeFi collateral levels had reached $9 billion.
Because of the increased interest in DeFi, Ethereum saw an increase in developers in 2020. Venture capitalists such as Andreessen Horowitz and Michael Novogratz have invested in DeFi. In 2022, The Economist looked at the future of digital finance.
Use cases for the technology
There are a number of interesting emerging use cases of the technology which include some of the following examples:
Asset management
DeFi projects enable individuals to manage a variety of different digital assets such as Cryptocurrencies (coins), NFTs, domains, and more.
There are also apps like Metamask which provide a way for users to store and manage their encrypted keys locally on their computers or web browsers via extensions.
P2P Loans and borrowing
Another type of functionality offered by some DeFi applications is the ability for individuals to offer loans to each other and include interest on top of what they borrow all through smart contracts.
Frequently Asked Questions around DeFi
What is the difference between DeFi and crypto?
Cryptocurrency refers to digital currencies built on top of a Blockchain decentralized network while DeFi refers to a whole concept around completely decentralized financial applications on the Blockchain. The value of Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Litecoin is stored within their own blockchain and will vary by each coin and the state of the market.
Cryptocurrencies may not be 100% decentralized and operate on a hybrid or private Blockchain foundation whilst DeFi by nature is fully decentralized.
Is DeFi like Bitcoin?
DeFi is concerned with developing decentralized applications that allow people to use their money without relying on a third party, whereas Bitcoin is concerned with developing a new type of digital currency that can be used for online transactions. Whilst they are different they both overlap in some of their goals and functionality namely using peer-to-peer technology and aiming to be decentralized.
Conclusion
We hope you found this resource page useful; if so, be sure to share it with anyone else who is interested in the technology and consider following us on our social profiles for more content like this.
For more information, please see our blog and range of business services, as well as the links below to other relevant content on our website.
Other related content from our website:
Financial technology (Fintech)
What is Tokenization in the context of Crypto?
Financial services website design & SEO services
Mining in cryptocurrency – What it is and how it works
What is Cryptography and how does it work?
What is Distributed Ledger Technology?
Summary of different companies & people involved in Crypto
What are Stablecoins and how do they work?
What is a Neobank and how does it work?
What is an ICO (Initial Coin Offering)
Getting started buying Bitcoin and other Crypto’s in Australia
What is the idea behind Web 3.0?
Cryptocurrency Market Analysis Definition
Blockchain Explorer Definition
Tips to choosing quality CFD trading apps in Dubai
What is Know Your Customer (KYC)?
What are Initial Exchange Offerings (IEOs)
Some of the best small business loan apps in Australia
List of platforms to help you accept Cryptocurrency payments on your website
Net worth calculator – online tool
Mortgage affordability calculator – online tool
Rankings/Buying guide to help you choose the best CFD brokers & apps in Australia
Crypto Mining Profitability Calculator
Leading Cryptocurrency exchanges for Indian users
Top-rated Crypto exchanges for South Africa
Some of the best Cryptocurrency exchanges & apps for Saudi Arabia
Some of the best small business loan providers for Perth
Top Alternatives to Swyftx for Australian Crypto users
Top-rated Alternatives to Etoro for Australian CFD traders
Different commercial loan brokers for Melbourne businesses
Collection of some of the best day trading platforms for Australians
ICO Marketing Solutions to help brands capture more online reach
CMC Markets Alternatives for Australian end-users wanting to start trading
Coinspot alternatives platforms Australians wanting to get started with Cryptocurrencies
Services to help you recover lost Crypto from your devices
List of some top Etoro alternatives for Australian forex traders
Top Sydney commercial loan brokers & platforms – curated list
What to look for when choosing a neobank app
Web3 Marketing Services By AGR Technology to help brands reach more users
Some of the best Cryptocurrency exchanges/apps for Canadians
Crypto Mining Conversion Calculator
Web3 Software Development Services
NFT Digital Marketing Services
(Guide) How to buy Cryptocurrency in Australia
Best places to earn interest on your Cryptocurrency assets
How to buy Bitcoin online or other Cryptos
Best stock market trading platforms Australia to buy shares
How to pay overseas contractors from Australia online
How to buy Etherium (Eth) in Australia
Bibliography/citation(s):
“Decentralized finance”, Wikipedia. 28-Sept.-2020. [Online]. Available: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decentralized_finance. [Accessed: 5-Mar.-2023].
“CeFi vs. DeFi — Comparing Centralized to Decentralized Finance” 16 June 2021, arxiv.org/abs/2106.08157. Accessed 6 Mar. 2023.
“Decentralized finance” Google Search, g.co/kgs/dx1TsY. Accessed 7 Mar. 2023.
Fiscal Nepal, Pros and cons of Centralized Finance (CeFi) and Decentralized Finance (DeFi), Fiscal Nepal (Aug. 25, 2021), https://www.fiscalnepal.com/2021/08/25/6194/pros-and-cons-of-centralized-finance-cefi-and-decentralized-finance-defi/.
![logo-new-23[1] logo-new-23[1]](https://agrtech.com.au/wp-content/uploads/elementor/thumbs/logo-new-231-qad2sqbr9f0wlvza81xod18hkirbk9apc0elfhpco4.png)
