What is Cross-Chain Communication? Exploring Blockchain Interoperability

Cross-chain communication refers to the ability for different blockchain networks to exchange information and value with one another. It addresses the challenge posed by the fact that most blockchains operate in isolation, effectively creating siloed ecosystems. To facilitate the vision of interoperability among these disparate systems, cross-chain technology enables the transfer of data, assets, and commands across various blockchain platforms, effectively allowing them to ‘speak’ to one another.
Cross-chain blockchain communication is critical in the context of cryptocurrency exchanges because it overcomes interoperability issues caused by the fragmented nature of blockchain networks. Cryptocurrency exchanges such as those in Australia, Bitcoin apps in New Zealand , Bitcoin exchange apps for Hong Kong and Crypto trading apps in Norway frequently operate on many blockchains, each with their own set of rules and standards. Cross-chain communication allows for seamless asset interactions and transfers between these varied blockchain ecosystems. For example a user on a platform such as Coinbase can buy SOL which is a Cryptocurrency native to the Solana Blockchain and then trade this for Bitcoin or another asset and seamlessly trade assets that are from different blockchain networks.
This capability improves the efficiency and liquidity of cryptocurrency exchanges by allowing users to trade and transfer assets across several blockchains without the use of intermediaries. It supports a more linked and inclusive financial ecosystem, resulting in a better user experience and increased acceptance of cryptocurrencies. As a result, cross-chain communication is critical to influencing the future of decentralized finance (DeFi) and increasing its accessibility to the public.
The development of these communication protocols is driven by the need for a more integrated blockchain landscape, where users and services can interact across platforms without the barriers currently present. By leveraging this technology, the efficiency, utility, and potential of blockchain applications are greatly enhanced. It allows for a multi-token and multi-chain environment where transactions and smart contracts can go beyond the confines of a single chain, paving the way for innovative use cases and applications.
Key Takeaways
- Cross-chain communication is crucial for interoperability between independent blockchains
- It allows different blockchain networks to exchange information, assets, and commands
- This technology is key to expanding blockchain applications, enhancing efficiency, and enabling innovative use cases
Understanding Cross-Chain Communication (Video explainer on the topic):
The following video is from a project that aims to create cross-chain communication and explains how this works. Cross-chain communication refers to the technology which enables information and value exchange between different blockchain networks. This is an essential capability that addresses the limitation of single blockchain ecosystems, permitting a more expansive and interconnected blockchain environment.
The Need for Interoperability
Blockchain interoperability is the foundation that allows decentralized applications (DApps) and tokens to interact across different blockchain platforms. This interaction is imperative because it enhances value transfer, data sharing, and feature execution between disparate blockchain systems. Without interoperability, blockchains would continue to operate in isolation, leading to fragmented markets and underutilized resources.
Mechanisms of Cross-Chain Communication
The mechanisms of cross-chain communication facilitate the exchange and understanding of information across multiple blockchains. These methods range from basic notary schemes to more complex hash-locking and distributed private key control. In a notary scheme, trusted entities known as notaries verify cross-chain transactions. Meanwhile, hash-locking involves the creation of a condition that must be met for a transaction to complete. Additionally, distributed private key control leverages multi-signature contracts which require consensus among multiple parties for execution.
Blockchain interoperability and cross-chain technology are rapidly evolving to meet the growing demand for integrated systems. Decentralized applications can benefit from these advancements by gaining access to a wider array of features and liquidity pools from multiple token ecosystems. As a result, users can enjoy seamless transactions and services despite using different blockchain platforms.
Technologies Enabling Cross-Chain Communication
Cross-chain communication is pivotal for interoperability among different blockchain networks. It involves several sophisticated technologies designed to facilitate the seamless transfer of value and information. This video explains some of the technologies helping to enable it.
Blockchain Bridges
Blockchain bridges, also referred to as cross-chain bridges, are integral for connecting blockchains to enable asset transfers and information exchange. Bridges may be trust-based, relying on intermediaries, or trustless, which use smart contracts to automate the process. Bridges enhance interoperability and can be either centralized, involving a single entity’s control, or decentralized, where control is distributed across multiple parties.
Atomic Swaps
Atomic swaps allow for the exchange of cryptocurrencies between different blockchain protocols without the need for an intermediary. Occupying a crucial role in cross-chain communication, these swaps use smart contracts that can automatically execute or reverse the transaction to ensure that both parties fulfill the agreed-upon terms. This technology is key for creating a trust-less exchange environment.
Relays and Oracles
Relays are mechanisms that allow blockchains to verify and integrate transactions from other networks. They strengthen the security and functionality of cross-chain operations. Oracles, on the other hand, provide real-world data to smart contracts on the blockchain and are instrumental in verifying conditions within atomic swaps and bridges. Both relays and oracles serve as communication layers that offer information necessary for the successful execution of cross-chain transfers.
Security and Risks in Cross-Chain Communication

In the landscape of blockchain technology, the security of cross-chain communication stands as a critical element. As different blockchains attempt to interact, the integrity and trustworthiness of these connections are paramount, requiring robust security models and effective risk management practices.
Security Models
Cross-chain communication demands security models that can effectively prevent malicious activities. One approach is the use of trust assumptions where validators—entities responsible for verifying transactions—play a pivotal role. These models often employ a corruption threshold meaning a certain proportion of validators must remain honest for the system to function securely.
Security properties are critical, incorporating mechanisms such as cryptographic proofs and consensus algorithms designed to ensure the validity and immutability of inter-blockchain transactions. For example, the research discusses mechanisms that aim to reduce the security risks of communication between chains, typically through relay or hash locking techniques. Another study analyzes cross-chain communication protocols in terms of security, with respect to various threats identified in cross-chain technologies.
Risk Management
Effective risk management in cross-chain communication serves to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities. Strategies here entail continuous monitoring of cross-chain activities, incident response planning, and regular security audits. Understanding and managing the risks associated with cross-chain transactions involve analyzing the entire network’s validation process to secure the overall chain network from potential exploits.
Thorough risk management also looks into the effectiveness of security protocols, assessing them against an evolving landscape of threats. For instance, Cambridge University research stresses the importance of having a thorough understanding of potential security threats to maintain a fortified cross-chain communication framework. Additionally, considering smart contract-driven cross-chain communication, experts recognize that existing cryptography techniques can be pivotal to safeguard against security threats.
Cross-Chain Protocols and Standards
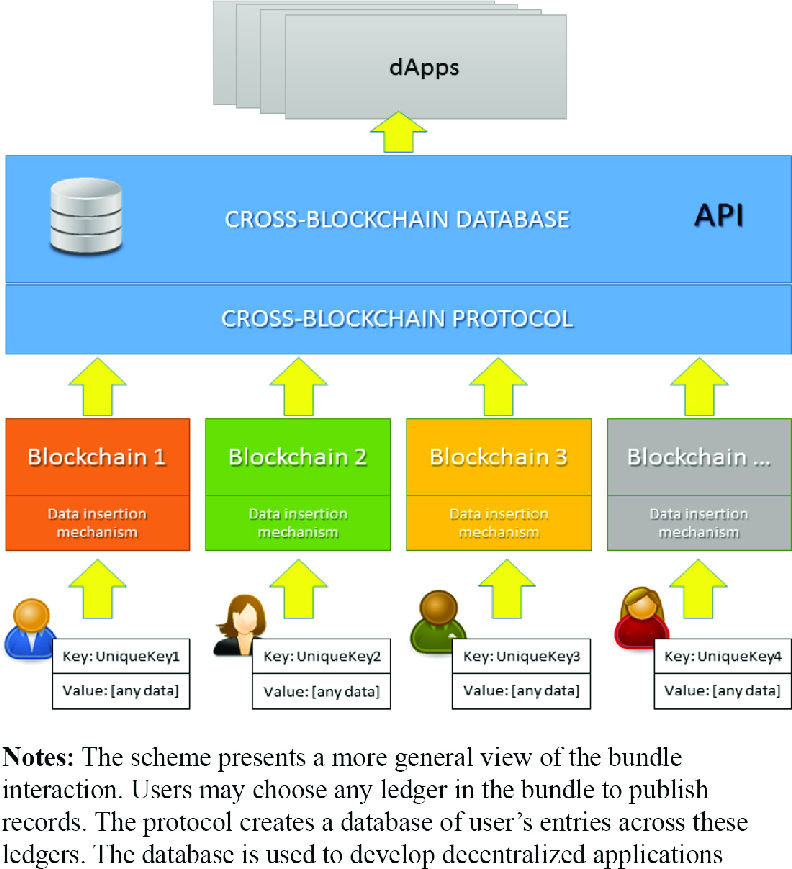
Cross-chain communication is essential for blockchain interoperability, allowing diverse blockchain networks to exchange information and value. Protocols and standards have been developed to facilitate these cross-chain interactions, focusing on interoperability, blockchain-agnostic frameworks, and shared governance.
Interoperability Protocols
Interoperability protocols are the foundations for enabling blockchains to connect and communicate. They provide the necessary rules and mechanisms for transmitting data and assets securely and efficiently between different blockchain networks. These protocols are often blockchain-agnostic, designed to function across multiple platforms and not restricted to a specific blockchain environment. For platform developers, this means the ability to build and deploy applications that can operate across a variety of blockchain ecosystems without being siloed within any single one.
Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP)
Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) is a specific standard aimed at enhancing the interoperability of different blockchain networks. CCIP establishes a shared governance model, which is crucial in maintaining the decentralized nature of blockchains while managing the cross-chain communication process. The protocol outlines how information, transactions, and smart contracts can interact across distinct blockchains in a trustable and secure manner. Implementing CCIP can be a significant step forward for platform developers looking to leverage the full potential of a connected blockchain ecosystem.
Use Cases and Applications
Cross-chain communication serves as a critical bridge linking various blockchain networks, expanding their capabilities and providing new opportunities for interoperability. The following sections explore how this technology is applied in specific areas, enhancing the functionality and reach of digital assets and decentralized services.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi platforms benefit substantially from cross-chain communication, as it enables users to engage in token transfers and asset management across different blockchains. One notable application is facilitating liquidity pools that operate on multiple chains, thereby improving accessibility and capital efficiency. Users are able to seamlessly exchange tokens between distinct DeFi ecosystems, which were previously isolated, leading to enhanced market liquidity and fostering a more integrated financial landscape.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
NFTs stand to gain from cross-chain technology by allowing for more fluid movement and interaction. Cross-chain solutions can enable these tokens to be transferred and accessed across different blockchain environments. This means that digital collectibles or in-game items minted on one blockchain can potentially be used or traded on another, broadening the horizons for collectors and creators alike. This interoperability is pivotal in propelling the NFT market forward, as it provides a wider canvas for creativity and utility.
General Applications
Beyond DeFi and NFTs, cross-chain applications are diverse and impactful. They can include, but are not limited to, enhancing supply chain management solutions, enabling cross-platform identity verification, and expanding voting mechanisms. These applications demonstrate the broad potential of cross-chain communication to streamline and secure a wide array of operations. Real-world assets can also be tokenized on one blockchain and then used on another, opening up a plethora of use cases for businesses looking to adopt blockchain technology.
Conclusion
We hope you found this page to be helpful, if so be sure to share it on social media and also check out the links below to other content on our blog and technology glossary.
Other content you may like from our glossary & blog:
Altcoin (Alternative crypto coins)
Cryptocurrency Market Analysis Definition
Digital Wallets / Smart Wallets
DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization)
Beginners guide to start buying Bitcoin in Australia
Online utility to track Crypto prices and help you decide the best Cryptocurrency to buy right now
Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT)
Fintech (Financial Technology)
Some of the best small business loan providers in Australia
How can you accept Cryptocurrency payments on your eCommerce website?
Guide to choosing the best CFD Broker Apps for the UAE
What are Initial Exchange Offerings (IEOs)
Buyers guide / Comparison of Cryptocurrency platforms for Singapore users
Net worth calculator – online tool
Mortgage affordability calculator – online tool
Buyers guide to choosing some of the top CFD brokers & apps in Australia
Leading Cryptocurrency exchanges for Indian users
Top-rated Crypto exchanges for South Africa
Some of the best Cryptocurrency exchanges & apps for Saudi Arabia
Some of the best small business loan providers for Perth
Top Alternatives to Swyftx for Australian Crypto users
Top-rated Alternatives to Etoro for Australian CFD traders
Some of the best Cryptocurrency exchanges/apps for Canadians
CMC Markets Alternatives for Australia
Coinspot alternatives platforms Australian Crypto users
Cryptocurrency wallet data recovery services by AGR Technology
Web3 Marketing Services By AGR Technology
Some of the best loan providers for Melbourne businesses
The best day trading applications/platforms for Australians
Top Sydney commercial loan brokers
Top Forex trading brokers for Canadian users
Top Etoro alternatives for Australian forex traders
What to look for when choosing a neobank app
Some of the leading forex trading platforms for New Zealand users
Web3 Software Development Services
NFT Digital Marketing Services
(Guide) How to buy Cryptocurrency in Australia
Best places to earn interest on your Cryptocurrency assets
How to buy Bitcoin online or other Cryptos
Best stock market trading platforms Australia to buy shares
How to pay overseas contractors from Australia online
How to buy Etherium (Eth) in Australia
Frequently Asked Questions
How is cross-chain communication implemented in blockchain technology?
Cross-chain communication is typically put into practice through protocols that allow the exchange of information and value between distinct blockchain networks. These protocols are designed to be secure, ensuring that transactions are verified and consistent across the chains involved. Atomic swaps and relay chains are common methodologies in this space.
What are some examples of cross-chain interoperability projects?
Examples of cross-chain interoperability projects include Polkadot, which enables different blockchains to transfer messages and value in a trust-free fashion. Likewise, Cosmos provides a network of blockchains that can communicate with each other through the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol.
How does a cross-chain bridge function to connect different blockchains?
A cross-chain bridge provides a means for two distinct blockchains to interact, allowing the transfer of assets and information. It operates through smart contracts that manage the locking and unlocking of funds, thereby maintaining the integrity and continuity of the asset across chains.
In what ways does cross-chain interoperability enhance cryptocurrency transactions?
Cross-chain interoperability expands the utility of cryptocurrencies by enabling asset transfers between different blockchain systems. This approach facilitates a more interconnected and flexible ecosystem, allowing for more versatile financial operations and increasing the potential for innovation in the space.
What distinguishes cross-chain technology from traditional blockchain structures?
Traditional blockchain structures typically function as standalone ecosystems. Cross-chain technology, on the other hand, connects these isolated environments, enabling them to interoperate and share value, a capability that is essential for achieving the full potential of decentralized applications.
Can smart contracts operate across different blockchain networks, and if so, how?
Yes, smart contracts can operate across different blockchain networks through cross-chain communication protocols. This is achieved by creating interconnected smart contracts that are executed in a coordinated manner across chains, allowing them to perform operations beyond the scope of their native blockchain.
Source(s) cited:
[Online]. Available at: https://th.bing.com/th/id/OIP.XDLFgSTMqgFS1FT0CkUWGgHaEK?rs=1&pid=ImgDetMain (Accessed: 5 January 2024).
“Research Gate” www.researchgate.net/profile/Oleksii-Konashevych/publication/347115016/figure/fig14/AS:968831111553034@1607998745791/Cross-blockchain-protocol-scheme.png. Accessed 7 Jan. 2024.
D. Phillips, “What is Cosmos Network (ATOM), the Internet of Blockchains?”, Decrypt. 5-Mar.-2021. [Online]. Available: https://decrypt.co/resources/cosmos. [Accessed: 7-Jan.-2024].
![logo-new-23[1] logo-new-23[1]](https://agrtech.com.au/wp-content/uploads/elementor/thumbs/logo-new-231-qad2sqbr9f0wlvza81xod18hkirbk9apc0elfhpco4.png)