Introduction

Alternative currencies or altcoins as they are known for short refer to any type of Cryptocurrency that is different from Bitcoin which was the first public Cryptocurrency coin in existence.
Altcoins frequently differ from Bitcoin in terms of functionality, such as Litecoin’s ability to execute a block every 2.5 minutes and Ethereum’s smart contract functionality. In 2016, Ethereum has arguably one of the most following of any altcoin and was the most widely used blockchain in 2020. Altcoin market rallies are commonly referred to as an “alt season”.
Some people consider altcoins to be anything separate from Bitcoin or Ethereum as these are the 2 largest cryptocurrencies at the time of publishing and the majority of coins and blockchain projects are built on either of these 2 blockchains.
Numerous altcoins have become very popular amongst crypto enthusiasts and investors alike and various altcoins be bought and sold on different crypto exchange platforms.
Also, read:
Top Crypto Exchanges for Norway
Best crypto exchanges in New Zealand
Some of the best apps to buy/sell Crypto in Dubai
Best Crypto exchanges for trading & buying in Taiwain
Best Cryptocurrency platforms for buying, trading and selling in Singapore
Key takeaways about altcoins
- Altcoins can be bought and sold across popular exchanges such as Binance and Crypto.com
- Altcoins can often be mined with specialized hardware and software which rewards miners with a small amount of crypto for processing transactions on the blockchain. This is an exception however with some altcoins like Ethereum which adopt a different method called proof of stake.
- Altcoins are considered riskier than their more established counterpart and may or may not actually utilize proper blockchains. Scams or worthless altcoins are commonly referred to as shitcoins
- Altcoins can be used in tandem with Bitcoin: Altcoins can supplement established coins like Bitcoin in a variety of ways. Some altcoins, for example, are intended to be faster or more efficient than Bitcoin, while others offer additional functionality such as smart contracts for validation.
What are some common altcoin examples?
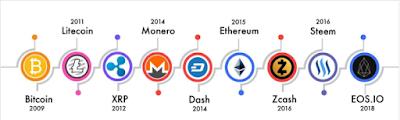
There are literally thousands of different altcoins out there in the world of crypto with new ones coming online all the time. Here are a few notable ones and a short concise description of each one.
Ethereum
![]()
A decentralized blockchain with smart contract capabilities is Ethereum. The platform’s own cryptocurrency, Ether, has a market valuation that is only surpassed by that of Bitcoin. It was created in 2013 by programmer Vitalik Buterin and is open-source software.
Crowdfunding for development work started in 2014, and on July 30, 2015, the network launched. Anybody can publish permanent and unchangeable decentralized applications on Ethereum, allowing users to communicate with them.
Applications for decentralized finance (DeFi) offer a wide range of financial services without the need for conventional financial intermediaries. NFTs, which are distinctive tokens that reflect ownership of an associated asset or privilege, are another feature that users of Ethereum can develop and exchange.
Proof-of-work (PoW) was replaced with a new consensus mechanism for Ethereum on September 15, 2022. This new consensus is known as proof of stake and was known as “The Merge” and reduced energy usage by approximately 99%.
Ripple (often referred to as XRP)

Ripple is a real-time gross settlement system, currency exchange network, and remittance network founded in 2012 by Ripple Labs Inc. It is based on an open-source distributed protocol and accepts tokens representing fiat currency, cryptocurrency, commodities, or other units of value.
It claims to be able to conduct “secure, instantaneous, and nearly free global financial transactions of any size with no chargebacks.” The US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) sued Ripple Labs and two of its executives in December 2020 for selling XRP tokens, which the SEC classified as unregistered securities.
Ripple was created by Jed McCaleb and built by Arthur Britto and David Schwartz, who approached Ryan Fugger, who had developed a system called OpenCoin that would eventually become Ripple. The company also created its own digital currency, XRP, to allow financial institutions to transfer money with minimal fees and wait time.
Over 100 banks had signed up by 2018, but the majority were only using Ripple’s XCurrent messaging technology, avoiding the XRP cryptocurrency due to its volatility issues. Ripple is based on a shared ledger, which is a distributed database that stores information about all Ripple accounts. Ripple instantly validates accounts and balances for payment transmission and sends payment notifications in a matter of seconds.
Ripple, being an altcoin, operates on a system that facilitates payments that cannot be reversed, and therefore chargebacks are not possible. The consensus verification system behind Ripple is predominantly maintained and updated by Ripple Labs. The unique features of Ripple gained significant recognition in 2014 when it was allowed access to the US banking system due to concerns over security and the absence of a well-regulated environment for traditional payment methods.
Litecoin

Litecoin is a Bitcoin-inspired decentralized peer-to-peer cryptocurrency and open-source software project. It uses a slightly modified version of the Bitcoin codebase, which results in lower transaction fees, faster transaction confirmations, and faster mining difficulty retargeting.
It added optional privacy features via soft fork through the MWEB upgrade in 2022. Litecoin differs from Bitcoin in that it employs a different proof-of-work algorithm, Scrypt, and is jointly mined with Dogecoin.
It has an 84,000,000 maximum circulating supply and retargets its mining difficulty every 2016 block. In May 2022, MWEB optional privacy was added to Litecoin’s base layer, and third-party vendors providing Litecoin point-of-sale infrastructure include Verifone, BitPay, and Coingate.
Monero (often referred to as XMR)

Monero is another popular altcoin that has existed since 2013 and is focused on privacy features inside its blockchain to provide added layers of security to transactions.
Here’s a short YouTube video that is a mirror of an official explanation from the Monero website:
Why do altcoins exist?

Due to the open-source nature of Bitcoin, the first ever mainstream recognized cryptocurrency code is publically accessible which makes it possible for 3rd party developers and individuals to build their own projects.
Altcoins have as a result grown for a variety of reasons such as a desire for better efficiency, alternative technical protocols, and other core goals that differ by the project such as Monero which puts more emphasis on privacy, and other projects like Filecoin which are intended to be used for utilities regarding file storage and decentralized file sharing.
Pros & cons of altcoins

Advantages:
- Altcoins offer the potential for more diversification for investors who wish to buy crypto assets
- Altcoins are cheaper compared to bigger mainstream currencies like Bitcoin which has become very expensive since its inception and mainstream interest
- Improves upon traditional cryptocurrencies with additional features and innovations from developers
- When compared to Bitcoin, some altcoins have a lower entry barrier for mining or investment. This can help new end-users get started and makes the entire space more accessible.
- Altcoins often have faster transaction times
Disadvantages:
- Due to being less popular the market caps will be lower and generally not as valuable in comparison to mainstream coins
- Can sometimes be difficult to determine use cases for the projects
- Less liquidity compared to established coins like Bitcoin
- Many new altcoins are scams or have lost developer and community interest over time making them less valuable and in other cases completely worthless
Conclusion
All up we hope you found this page to be helpful about altcoins and how they fit into the large world of crypto and blockchain technologies.
Be sure to check out our blog, links below, and the range of business services we offer for more.
Related terms from our glossary:
List of some of the best Crypto exchanges in Hong Kong
DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization)
FinTech (Financial technology)
Staking pools – What are they and what are the benefits?
DApps – Definition & information
Financial services websites and SEO services
Central Bank Digital Currencies
How to buy Bitcoin in Australia
What are some of the best Cryptocurrencies to buy?
How to accept Cryptocurrency payments on a website
Cryptocurrency market analysis
What are Initial Exchange Offerings (IEOs)
Top SMB loan platforms in Australia
Mortgage affordability calculator
Comparison of the best CFD brokers/apps in Australia
Some of the best Cryptocurrency exchanges for Indian users
Best Crypto exchanges for South Africa
Top Crypto exchanges for Saudi Arabia
Alternatives to Swyftx for Australian Crypto users
Alternatives to Etoro for Australian CFD traders
Some of the best Crypto exchanges for Canadians
Top CMC Markets Alternatives in Australia
Coinspot alternatives for Australian Crypto traders
Crypto wallet recovery services by AGR Technology
Web3 Marketing Services & Solutions For Brands
Curated summary of some of the best loan providers for Melbourne businesses
List of some of the best day trading applications for Australians
Top Forex trading platforms & brokers for Canadians
Top Etoro alternatives for Australian forex traders
What to look for when choosing a neobank app
Some of the best forex trading apps for New Zealand
*Bibliography:
Cryptocurrency. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cryptocurrency. Published August 8, 2012. Accessed April 8, 2023.
J. Doe, “Ethereum’s Switch to Proof of Stake Changes Securities Risks”, 4-Apr.-2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.quinnemanuel.com/the-firm/publications/ethereum-s-switch-to-proof-of-stake-changes-securities-risks/. [Accessed: 9-Apr.-2023].
“What is Monero (XMR)?” Getmonero.org, The Monero Project, www.getmonero.org/get-started/what-is-monero/. Accessed 9 Apr. 2023.
(2005). Ripple (payment protocol) [Online]. Wikipedia. Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ripple_(payment_protocol) (Accessed: 9 April 2023).
Ethereum. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ethereum. Published January 27, 2014. Accessed April 9, 2023.
“Global Cryptocurrency Market Charts”, CoinMarketCap. [Online]. Available: https://coinmarketcap.com/charts/. [Accessed: 9-Apr.-2023].
“Litecoin” Wikipedia, 20 Oct. 2012, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Litecoin. Accessed 9 Apr. 2023.
Mohamed. “The Beginner’s Guide To Altcoins” Tech Blog, 21 Aug. 2022, myblog.sites.ucsc.edu/2022/08/21/the-beginners-guide-to-altcoins/. Accessed 9 Apr. 2023.
“Money in Colonial Times” www.philadelphiafed.org/education/money-in-colonial-times. Accessed 9 Apr. 2023.
![logo-new-23[1] logo-new-23[1]](https://agrtech.com.au/wp-content/uploads/elementor/thumbs/logo-new-231-qad2sqbr9f0wlvza81xod18hkirbk9apc0elfhpco4.png)