Introduction

The process of managing a company’s or organization’s interactions with its customers is known as customer relationship management or CRM as it’s abbreviated for short. CRM systems collect data from a company’s website, phone, email, live chat, marketing materials, and, more recently, social media and use it to improve marketing and customer relationships.
They ultimately enable businesses to learn more about their target audiences and how to best cater to their needs, resulting in customer retention and sales growth.
Major components of a CRM
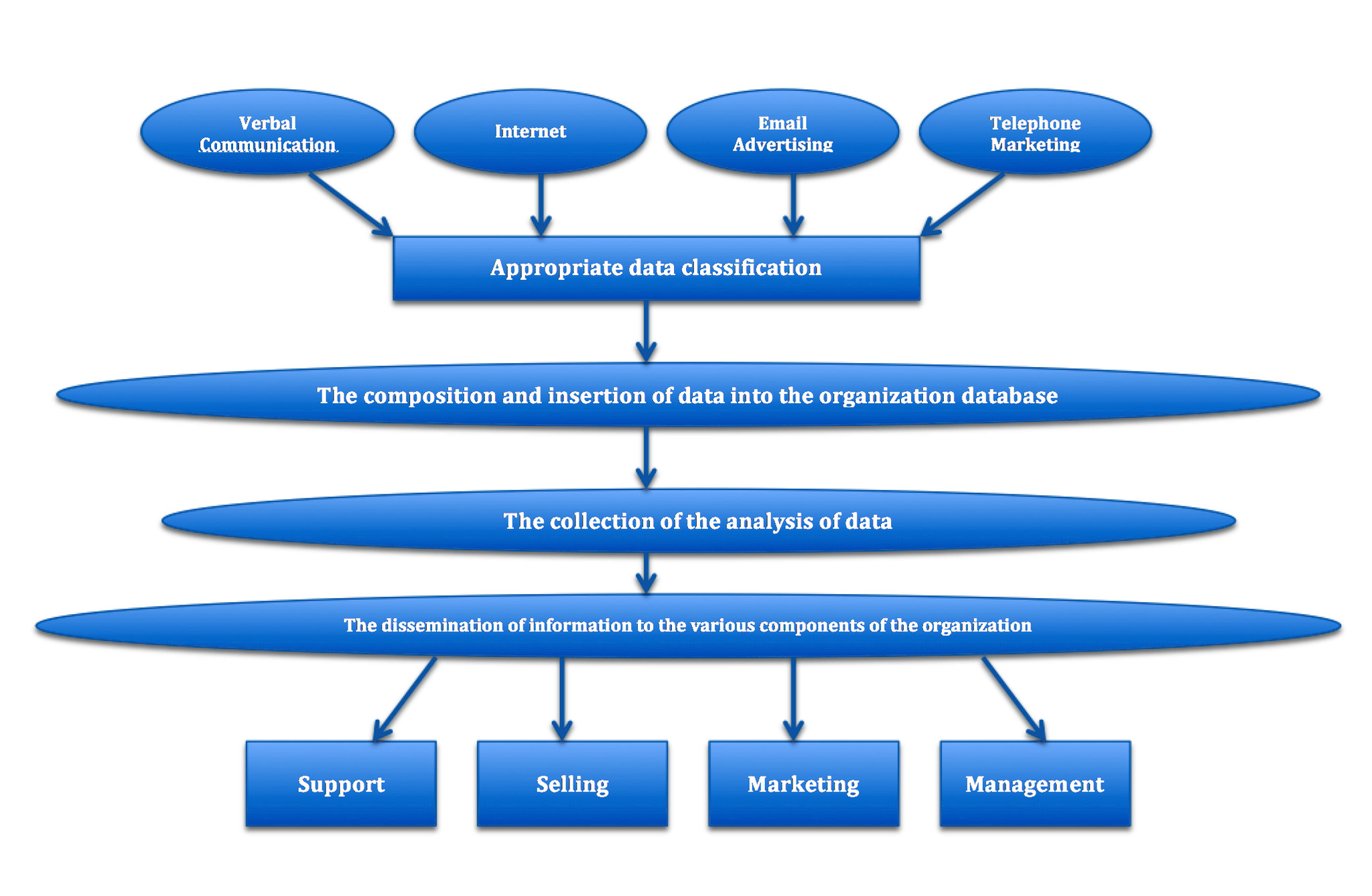
Some of the main components of CRM’s consist of marketing to build and manage customer relationships, observing relationships as they mature through distinct stages, managing these relationships at each stage, and recognizing that the distribution of the value of a relationship to the firm is not homogeneous.
As firms build and manage the relationships with their customers through marketing, they may need tools to assist with organizational design, incentive schemes, customer structures, and more.
Businesses will benefit from seeing the interaction of multiple relationships as connected transactions if the distinct phases of a CRM are recognized. The final CRM factor emphasizes the significance of CRM technologies by accounting for the profitability of customer relationships.
A company may be able to devote different resources and amounts of attention to different types of customers by studying their specific spending habits, thereby addressing their different needs.
Companies may be skilled at obtaining demographic data such as gender, age, income, and education and combining it with purchasing information to classify customers into profitability categories, but this is merely an industrial view of customer relationships.
A lack of relational intelligence indicates that businesses still view customers as resources to be used for up-sell or cross-sell opportunities, rather than people seeking intriguing and personalized interactions.
Other components include:
Data warehousing

The technology of data warehouses is used to aggregate transaction data, combine it with CRM solutions, and provide critical performance indicators and analytics.
Strategic opportunity management:

Opportunity management assists the organization in managing unanticipated growth and demand, as well as in putting in place strong forecasting models in order to integrate sales history and their estimates.
eCommerce operations

CRM systems for eCommerce exist which are primarily focused on marketing automation tasks such as cart rescue, email re-engagement, and user experience in an effort to improve sales.
Some background history of CRM software
Customer relationship management emerged in the early 1970s, when customer satisfaction was measured through annual surveys or front-line questions. Businesses had to rely on standalone mainframe systems to automate sales at the time, but technological advancements allowed them to categorize customers in spreadsheets and lists.
The Farley File was a comprehensive set of records detailing political and personal facts on people FDR and Farley met or were supposed to meet. It was developed by Franklin Roosevelt’s campaign manager, James Farley, and was one of the most well-known precursors to modern-day CRM systems.
People FDR met were impressed by his “recall” of facts about their family and what they were doing professionally and politically when he used it. Kate and Robert D. Kestenbaum pioneered the concept of database marketing in 1982, namely the use of statistical methods to analyze and collect customer data.
Pat Sullivan and Mike Muhney released ACT!, a customer evaluation system based on the principle of a digital Rolodex that offered a contact management service for the first time, around 1986.
This included incorporating CRM features such as sales force automation or extended customer service such as inquiry & activity management into their ERP software. Customer relationship management became increasingly popular in 1997 and onward as a result of the efforts of Siebel, Gartner, and IBM collectively.
Leading CRM products were enhanced with shipping and marketing capabilities between the years of 1997 and 2000. A mobile based CRM application called Siebel Sales Handheld was released by Siebel in 1999.
Types of CRM’s in use:
On-premise solutions
An on-premise CRM is housed internally within a corporate network and can be either an off the shelf product or custom developed by a software developer/company.
This approach can also be confined to an individual workstation and isn’t connected to the internet. On-premise solutions are typically deployed in industries where security of information is very critical and strict compliance is necessary.
Cloud based CRM (SaaS)
A cloud based CRM can be accessed remotely from any device and on any network making it a convenient option and much more scalable.
This approach is typically offered as a subscription on a monthly or annual basis to provide licenses to use the software.
Hybrid solution
A hybrid CRM is one that is built in house and uses custom code but is hosted on cloud infrastructure so that it can be accessed remotely and across multiple devices such as mobiles and tablets.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
What features are typically included in CRM technology?
CRM platforms typically includes features such as contact management, sales automation, marketing automation, customer service and support, analytics and reporting as well as collaboration and communication tools.
How do I choose the right CRM technology for my business?
Consider factors such as your company’s size, industry, specific needs and goals, budget, and the features and capabilities provided by various CRM solutions when selecting CRM technology. It can also be beneficial to investigate free trials available and experiment with entering some test data before gathering feedback from employees or other business stakeholders to determine the platform that has all of the required functionality as well as the user interface that is most appropriate for the people using it.
Conclusion
We hope you found this information to be helpful! If so please consider sharing this on social media with anyone you think would be interested.
Do you want to have your own CRM built? Contact AGR Technology today to find out how our digital solutions such as Software and Web Development can help your business grow.
Also be sure to follow us for updates and check out our blog, videos and online tools.
Related terms from our glossary:
IaaS (Infrastructure As A Service)
Learning Management System (LMS)
Source(s) cited:
Bgrigorov, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
“Customer relationship management” Wikipedia, 1 Nov. 2001, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Customer_relationship_management. Accessed 18 June 2021.
Sienanews.it. 2021. [online] Available at: <https://www.sienanews.it/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/gctv-crm.jpg> [Accessed 19 June 2021].
![logo-new-23[1] logo-new-23[1]](https://cdn-ihdfn.nitrocdn.com/eZVJvoSTyVixkEUySRKiaseNtUlmgCyu/assets/images/optimized/rev-0174fc5/agrtech.com.au/wp-content/uploads/elementor/thumbs/logo-new-231-qad2sqbr9f0wlvza81xod18hkirbk9apc0elfhpco4.png)