Introduction

(A common PC motherboard of a desktop tower)
In computing the CMOS is a small on-board battery powered device attached to the motherboard which stores information about your hardware settings and your BIOS as well as the system time and date.
The abbreviation CMOS stands for Complimentary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor.
Resetting the CMOS
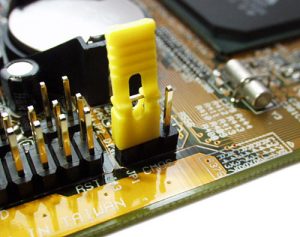
(Image sourced from Stackexchange via Creative commons)
The CMOS battery can often be reset in the event that you forgot your BIOS password, it can be done by re-seating it onto the board after approximately 5 minutes. Alternatively many motherboards have a jumper as shown in the above image.
Pulling the top off for approximately 5 minutes and reconnecting it can also reset the CMOS unit and restore the BIOS to factory defaults.
(video guide coming soon)
Average lifespan & devices which use CMOS
The average lifespan of one of these batteries is approximately 10 years which can vary depending on the condition of the computer, its environment and age.
The following devices utilize one of these batteries:
- Digital logic circuits
- Static RAM or SRAM for short
- Microprocessors
- Micro-controllers
Other names for CMOS

(An image shown above of a CMOS battery)
The CMOS battery is sometimes referred to by different names across different websites and computer manuals. Some of the alternate names for the CMOS battery include the following: Real-Time clock (RTC), CMOS RAM, Non-volotile memory or NVRAM and lastly Complementary-Symmetry metal-oxide-semiconductor or COS-MOS for short.
Apple Macintosh equivalent

On a macOS system the equivalent to the CMOS is PRAM which stands for parameter RAM.
Conclusion
Hopefully this entry has helped you learn more about the CMOS component in your computer. Be sure to share this page with your friends if you found it useful.
Follow AGR Technology for more updates on YouTube, Facebook and Twitter for more updates or check out other entries on the I.T glossary.
More terms from our glossary:
![logo-new-23[1] logo-new-23[1]](https://agrtech.com.au/wp-content/uploads/elementor/thumbs/logo-new-231-qad2sqbr9f0wlvza81xod18hkirbk9apc0elfhpco4.png)