
Ever wondered what those helpful assistants popping up on websites are? They’re chatbots – computer programs designed to simulate human conversation through text or voice interactions. These AI-powered tools can understand your questions and respond with relevant information, even when your grammar isn’t perfect.
Chatbots have become ubiquitous in our digital world, appearing everywhere from Facebook Messenger and WhatsApp to smart speakers and workplace applications like Slack. They range from simple script-based programs that answer specific questions to sophisticated AI systems using natural language processing to handle complex conversations. For businesses, they reduce overhead costs while providing 24/7 customer service, making them valuable in both B2C and B2B environments.
They can be integrated into a number of different website platforms and either operate as standalone assistants or hook into platforms like Telegram, and the ones mentioned above depending on user preferences. Chatbots can also be custom developed by software companies for businesses that have very unique specific needs that are not available from off the shelf products.
What Is a Chatbot?
A chatbot is a computer program designed to simulate human conversation through text or voice interactions. These AI-powered tools communicate with users in a conversational manner, providing responses to queries and performing specific tasks without human intervention.
Chatbots operate via two primary methods: rule-based systems that follow predetermined guidelines or AI-driven models that utilize machine learning and natural language processing. The advanced AI chatbots can understand context, learn from interactions, and provide increasingly relevant responses over time.
Businesses incorporate chatbots across multiple platforms including Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp, SMS, and workplace messaging applications like Slack. They serve various functions from answering frequently asked questions to scheduling appointments and processing simple transactions.
Major tech companies have developed sophisticated virtual assistants that exemplify advanced chatbot technology, such as Apple’s Siri, Amazon’s Alexa, Google’s Gemini, and OpenAI’s ChatGPT. These intelligent virtual assistants handle complex conversations and automate relevant tasks for both consumers and enterprises.
The implementation of chatbot technology offers significant business advantages, including:
- Reduced overhead costs through automated customer interactions
- More efficient use of support staff time and resources
- 24/7 customer service availability without additional staffing
- Streamlined communication in both B2C and B2B environments
As AI technology continues to evolve, chatbots have transformed from simple scripted response systems to sophisticated conversational agents capable of understanding nuanced language, even when grammatically incorrect, and providing personalized assistance based on collected data.
How Do Chatbots Work?
Chatbots function through programmed systems that process user inputs and generate appropriate responses. The technology behind chatbots ranges from simple rule-based frameworks to sophisticated AI systems that can understand and simulate human conversation.
Rule-Based Chatbots
Rule-based chatbots operate on predefined patterns and scripts that match keywords in user inputs to specific responses. Created as early as 1966 with MIT’s ELIZA, these chatbots follow a pattern-matching approach where they recognize specific words or phrases and respond with preprogrammed answers. They’re unable to interpret context or intent beyond their programming and struggle with spelling mistakes or grammatical errors. Despite these limitations, rule-based chatbots remain useful for straightforward tasks with predictable user inputs, such as helping customers log tickets or navigating phone trees. Their simplicity makes them quicker and less expensive to develop than AI alternatives.
AI-Powered Chatbots
AI-powered chatbots utilize natural language processing (NLP) to understand user queries even when phrased imperfectly. These sophisticated systems learn from interactions and evolve over time, collecting data to improve their responses. Modern AI chatbots feature three key advantages: adaptability across various business functions, cost-effectiveness compared to human personnel, and 24/7 availability for instant customer assistance. With the emergence of large language models (LLMs), generative AI-powered chatbots can now produce human-like text for comprehensive responses. Hybrid models combine AI capabilities with menu-based functions, offering users the flexibility to either navigate through options or ask direct questions. These advanced chatbots require specialized development from AI engineers who build models using machine learning algorithms and NLP engineers who create programs capable of understanding human language nuances.
Types of Chatbots
Chatbots come in various forms, each designed to serve specific purposes across different platforms. These digital assistants range from simple text-based interfaces to sophisticated AI-powered systems that can understand natural language and perform complex tasks.
Voice Assistants
Voice assistants are AI-powered chatbots that primarily use speech recognition to interact with users through voice commands. Digital Personal Assistants (DPAs) like Google’s Assistant, Amazon’s Alexa, and Apple’s Siri fall into this category, offering hands-free convenience for everyday tasks. These sophisticated systems can create calendar appointments, provide weather updates, control smart home devices, play music, and even offer companionship. Voice assistants typically operate through smart speakers, mobile devices, and integrated systems in cars, creating a seamless interaction experience that mimics human conversation.
Social Messaging Chatbots
Social messaging chatbots integrate with popular messaging platforms like Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp, and SMS to engage with users in their preferred communication channels. Meta’s machine learning chatbot enables companies to interact with consumers directly through the Messenger application, facilitating transactions and information sharing. For example, users can purchase shoes from Spring, order Uber rides, or receive news updates from The New York Times without leaving the messaging interface. These bots excel at providing immediate responses to customer inquiries, streamlining purchasing processes, and delivering personalized content based on user preferences and previous interactions.
Customer Support Chatbots
Customer support chatbots serve as the first point of contact for users seeking assistance on websites and applications. These bots handle everything from directing customers to product pages and support articles to walking them through complex technical solutions. By replacing traditional automated telephone menus—known to cause customer dissatisfaction—they provide immediate, 24/7 support without human intervention. Many businesses implement these chatbots to reduce overhead costs, better utilize support staff time, and maintain consistent service quality. Advanced customer support chatbots can understand context, remember previous conversations, and seamlessly transfer complex issues to human agents when necessary.
Benefits of Chatbots for Businesses
Chatbots deliver significant advantages to organizations through automation, cost savings, and enhanced customer experiences. Businesses implementing chatbot technology see improvements across multiple operational areas while simultaneously meeting evolving consumer expectations.
Improved Customer Engagement
Chatbots transform passive customer interactions into proactive conversations that build stronger relationships. They engage website visitors at peak moments of interest through personalized exchanges tailored to individual needs. With visitor intelligence capabilities, chatbots identify site visitors and customize experiences based on previous interactions, building valuable information into future conversations. High-value accounts receive priority treatment with personalized greetings and direct paths to sales teams, ensuring important opportunities aren’t missed even when human staff are offline.
Cost Reduction and Efficiency
Chatbots represent a cost-effective one-time investment compared to developing cross-platform apps or hiring additional employees. They handle thousands—even millions—of customer interactions simultaneously without increasing operational expenses. By automating repetitive tasks like appointment scheduling, survey distribution, and employee workflow management, chatbots free human resources for more complex responsibilities. This automation reduces costly problems stemming from human error while decreasing user acquisition costs through instant response capabilities.
24/7 Availability
Unlike human representatives who require breaks and time off, chatbots provide continuous service without interruption. This constant availability ensures customers receive immediate support without waiting on hold for live representatives. Chatbots can initiate conversations, monitor website behavior, and respond within seconds at any hour—eliminating wait times completely. For international businesses or companies serving customers across time zones, this round-the-clock functionality maintains consistent service quality regardless of when customers reach out.
Common Chatbot Use Cases
Chatbots have revolutionized how businesses interact with customers across numerous industries. These AI-powered assistants handle specialized tasks ranging from answering basic inquiries to facilitating complex transactions, providing 24/7 support and personalized experiences.
Customer Service
Customer service chatbots serve as the frontline support for organizations, handling frequently asked questions and troubleshooting common issues. These contextual assistants grasp the nuance of customer inquiries, determine the correct meaning, and recall prior interactions to maintain relevance with repeat customers. They dramatically reduce response times from hours to seconds, efficiently managing high volumes of inquiries simultaneously. Customer service bots also escalate complex issues to human agents when necessary, creating a seamless support experience that combines automation with human expertise.
E-commerce and Retail
E-commerce chatbots transform online shopping by offering personalized product recommendations based on browsing history and purchase patterns. They streamline the purchasing process by guiding customers through product selection, answering questions about specifications, and facilitating checkout in a conversational manner. These transactional assistants also help recover abandoned carts by sending timely reminders and offering incentives to complete purchases. Major retailers implement chatbots to provide instant support for order tracking, returns processing, and product availability inquiries, enhancing customer satisfaction throughout the buying journey.
Healthcare
Healthcare chatbots provide critical support for patients and healthcare providers alike. They help patients find appropriate healthcare providers, book examinations, and manage appointment schedules with automated reminders. Medication management bots send timely alerts to patients about taking prescribed medications, improving treatment adherence. These conversational assistants also collect preliminary information before appointments, answer basic health questions, and provide aftercare instructions, reducing administrative burdens on medical staff. During public health crises, healthcare chatbots disseminate accurate information, conduct initial symptom assessments, and direct patients to appropriate resources and can be integrated into websites for healthcare providers.
Financial Services
Financial service chatbots assist customers with account management, transaction history, and basic banking functions through secure conversational interfaces. They guide users through complex processes like loan applications, insurance claims, and investment decisions by breaking them down into simple steps. These specialized assistants provide personalized financial advice based on spending patterns, savings goals, and investment preferences. They also enhance security through additional verification methods during sensitive transactions while alerting customers to unusual account activity. Financial institutions deploy chatbots to educate customers about new products, assist with budgeting, and provide real-time market updates through convenient messaging platforms.
Challenges and Limitations of Chatbots

Despite their numerous benefits, chatbots face significant challenges that impact their effectiveness. Understanding these limitations helps businesses implement chatbot solutions that truly enhance customer experiences rather than create frustration.
Technical Challenges
AI-enabled chatbot technology introduces obstacles that many organizations aren’t prepared to handle. While these bots learn from interactions to improve performance, this learning process can be costly if initial poor interactions drive customers away. For example, AI chatbots can hallucinate—producing completely fabricated or incorrect information that appears convincing but lacks factual basis.
The quality of a chatbot’s training data directly determines its performance capabilities. Incomplete or inaccurate datasets severely limit functionality and increase hallucination risks. Continuous improvement requires substantial resources, including:
- Advanced machine-learning infrastructure
- Ongoing performance monitoring systems
- Regular training data updates
- Technical expertise for maintenance
Security and Privacy Concerns
Chatbots must establish sufficient trust for users to share personal information. Organizations implementing chatbots face several security challenges:
- Designing systems that request only relevant user data
- Ensuring secure data transmission protocols
- Implementing robust protection against hackers targeting chat interfaces
- Managing compliance with international privacy laws
- Addressing intellectual property concerns with user-provided content
Traditional and generative AI chatbots present different security risks, from data leakage to confidentiality breaches and uncertain regulatory compliance across global jurisdictions.
Understanding User Intent
Chatbots struggle with the natural variations in human communication. Common understanding challenges include:
- Processing different sentence lengths, from brief commands to lengthy explanations
- Interpreting misspelled words, acronyms, and slang terms
- Adapting to unpredictable shifts in conversation direction
- Recognizing emotional context behind user messages
Natural language processing has inherent limitations that prevent chatbots from fully resolving these comprehension challenges, often resulting in misinterpretation of user needs.
Scope Limitations
AI excels at automating repetitive, straightforward processes but struggles with complexity. There are specific scenarios where chatbots encounter significant difficulties:
- Complex service issues involving numerous variables
- Problems requiring nuanced judgment or ethical considerations
- Situations where emotional intelligence is crucial
- Cases that fall outside their training parameters
When tasks extend beyond a chatbot’s capabilities, the results can negatively impact both businesses and customers, leading to frustration and reduced confidence in the technology.
Meeting Evolving User Expectations
User satisfaction presents an ongoing challenge for chatbot implementation. Users continuously expect improvements in chatbot performance, creating pressure for organizations to:
- Consistently update conversational flows
- Improve response accuracy and relevance
- Enhance personalization capabilities
- Create more natural, human-like interactions
This constant need for enhancement requires sustained investment and attention to ensure chatbots remain effective and don’t become outdated as user expectations evolve.
The Evolution of Chatbot Technology
The journey of chatbot technology spans over five decades, showcasing remarkable advancements in artificial intelligence and natural language processing. From simple pattern-matching programs to sophisticated conversational agents, chatbots have transformed how businesses and consumers interact with technology.
Early Beginnings (1960s-1990s)
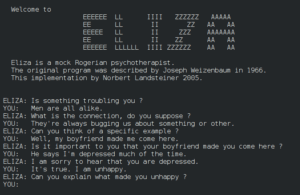
The first chatbot emerged in 1966 when Joseph Weizenbaum created ELIZA, a program that simulated a psychotherapist by rephrasing user input and asking questions. ELIZA’s convincing interaction style led many users to believe they were communicating with a human—a phenomenon later termed the “ELIZA effect.” This groundbreaking program laid the foundation for future developments despite operating on basic pattern matching and substitution techniques.
During the 1990s, developers created more advanced chatbots like ALICE (Artificial Linguistic Internet Computer Entity), which utilized Artificial Intelligence Markup Language (AIML). This XML schema specified conversation rules that helped simulate more natural-sounding dialogue, representing a significant step forward in conversational AI technology.
The Rise of Virtual Assistants (2000s-2010s)
The early 2000s marked a period of significant progress in AI and machine learning, culminating in the launch of virtual assistants that brought chatbot technology into mainstream awareness. In 2011, IBM’s Watson demonstrated the power of advanced AI by defeating Jeopardy champion Ken Jennings, showcasing unprecedented language processing capabilities.
By 2014, major tech companies had introduced personal assistants that millions now use daily—Apple’s Siri, Google Assistant, Microsoft’s Cortana, and Amazon Alexa. These virtual assistants incorporated voice recognition technology alongside text-based interaction, expanding the functionality and accessibility of conversational AI.
Modern AI-Powered Chatbots (2015-Present)
Today’s chatbots leverage neural networks inspired by the human brain, enabling them to self-learn as they encounter new dialogues and phrases. Unlike their predecessors that relied on predefined rules, modern chatbots continuously improve their response accuracy through machine learning algorithms and vast datasets.
The integration of chatbots into business operations has accelerated dramatically, with tools now available that allow non-technical users to create functional chatbots in as little as an hour. In 2023, platforms like Snapchat introduced features such as “My AI,” allowing users to customize their chatbot experience, name their virtual assistants, and engage in more personalized interactions.
Current chatbot technology falls into two primary categories:
- Rule-based systems: Operating on predefined patterns and responses
- AI-powered solutions: Using machine learning to understand context and generate human-like responses
As AI technology continues to evolve, chatbots are increasingly handling complex strategic tasks, freeing humans to focus on creative and innovative work. The transformation from simple phone trees to sophisticated digital assistants represents one of the most significant technological evolutions in human-computer interaction.
The Future of Chatbots
Chatbots are evolving rapidly, with several key developments shaping their future trajectory. These innovations are transforming how businesses and consumers interact with AI-powered conversation systems.
Enhanced Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing capabilities are becoming increasingly sophisticated in modern chatbots. Advanced algorithms now enable chatbots to understand context, detect sentiment, and respond more appropriately to complex queries. This improvement allows for more natural conversations that closely resemble human interaction. For example, newer systems can maintain context throughout multi-turn conversations and recognize subtle language nuances that earlier versions would have misinterpreted.
Integration with Voice Technology
Voice-enabled chatbots are gaining prominence as the technology behind speech recognition improves. This integration creates a seamless experience between text and voice interfaces, allowing users to switch between modalities based on their situation and preference. Major platforms like Google Assistant, Amazon Alexa, and Apple Siri demonstrate this convergence, handling both typed and spoken interactions with increasing accuracy.
Multimodal Capabilities
The next generation of chatbots is becoming multimodal, processing and generating not just text but also images, videos, and other media formats. These enhanced capabilities enable richer interactions and more comprehensive assistance. For instance, a multimodal chatbot can analyze an uploaded image of a product and provide detailed information about it while generating visual content to supplement its text responses.
Specialized Industry Solutions
Chatbots are becoming more specialized for specific industries and use cases. Healthcare chatbots focus on patient intake and symptom assessment, financial chatbots excel at transaction processing and financial advice, and retail chatbots specialize in product recommendations and inventory inquiries. This specialization allows for deeper domain expertise and more valuable interactions tailored to specific contexts.
Ethical and Responsible AI
The development of ethical frameworks for chatbot deployment is becoming a critical focus area. This includes addressing concerns around bias, privacy, transparency, and the responsible use of user data. Organizations are implementing guardrails to ensure chatbots provide accurate information, respect user boundaries, and maintain appropriate conversation parameters. The goal is creating trustworthy AI systems that users feel comfortable interacting with on a regular basis.
Ambient Computing Integration
Chatbots are becoming integral components of ambient computing environments where multiple devices work together seamlessly. In these ecosystems, chatbots serve as central interaction points that coordinate various smart devices and services. This integration enables more contextual awareness, with chatbots understanding not just the conversation but also the user’s physical environment and device ecosystem.
Personalization at Scale
Advanced chatbots now deliver hyper-personalized experiences by analyzing user data, past interactions, and behavioral patterns. This personalization creates more relevant and engaging conversations tailored to individual preferences and needs. For example, a chatbot might adjust its communication style, content recommendations, and response complexity based on its understanding of the specific user it’s interacting with.
The evolution of chatbots from simple rule-based systems to sophisticated AI-powered assistants highlights their growing importance in digital communication strategies. As these technologies continue to advance, chatbots will likely become even more integrated into our daily digital experiences, reshaping how we interact with information and services online.
Conclusion
Chatbots have transformed from simple rule-based programs to sophisticated AI-powered assistants that are reshaping how businesses and consumers interact. As technology advances I expect to see even more seamless integration of chatbots across industries with enhanced personalization capabilities.
The future looks promising with multimodal interactions voice technology integration and industry-specialized solutions becoming standard. While challenges exist around technical limitations privacy concerns and meeting user expectations the benefits far outweigh these hurdles.
Whether you’re looking to improve customer service reduce operational costs or provide 24/7 support chatbots offer a versatile solution that will continue to evolve with our digital landscape. The chatbot revolution isn’t just coming—it’s already here and rapidly changing how we communicate online.
Bibliography:
File:ELIZA conversation.jpg, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
![logo-new-23[1] logo-new-23[1]](https://agrtech.com.au/wp-content/uploads/elementor/thumbs/logo-new-231-qad2sqbr9f0wlvza81xod18hkirbk9apc0elfhpco4.png)