Introduction

(Example QR code that opens the AGR Technology website if scanned)
A QR code is a machine-readable optical label that contains data about the item to which it is attached. In practice, QR codes frequently include information for a locator, identifier, or tracker that leads to a website or application such as a booking system.
To store data efficiently, a QR code employs four standardized encoding modes (numeric, alphanumeric, byte/binary, and kanji).
An imaging device such as a camera can read QR codes, which are composed of black squares arranged in a square grid on a white background.
They are then processed using Reed–Solomon error correction until the image can be properly interpreted. The required data is then extracted from patterns in the image’s horizontal and vertical components.
QR code technologies can be integrated into different types of software in order to provide tracking and other functionality to end-users.
Some background history of the technology
Masahiro Hara of the Japanese company Denso Wave originally invented the QR code system back in 1994. The black and white pieces on a “Go board” inspired the initial design.
During the month of June 2011 approximately 14 million mobile users in the United States scanned a QR code or a barcode.
Since then there are various QR code generators are available as software or as online tools that are either free or require a paid subscription.
QR Code standards & specifications
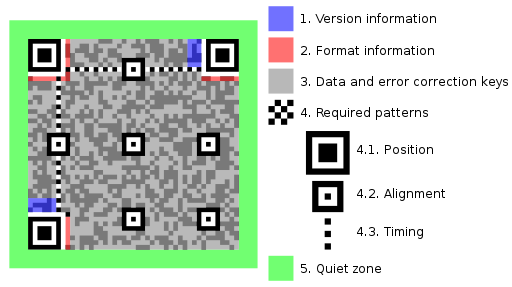
Image source: Bobmath, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
As far as QR codes are concerned, there are several standards for encoding data:
- October 1997 – AIM (Association for Automatic Identification and Mobility) International
- January 1999 – JIS X 0510
- June 2000 – ISO/IEC 18004:2000 Information technology – Automatic identification and data capture
- techniques – Bar code symbology – QR code (now withdrawn)
- Defines QR code models 1 and 2 symbols.
- 1st of September 2006 – ISO/IEC 18004:2006 Information technology – Automatic identification and data capture techniques – QR code 2005 bar code symbology specification (since withdrawn). This defines QR code 2005 symbols, an extension of QR code model 2. Does not specify how to read QR code model 1 symbols, or require this for compliance.
- 1 February 2015 – ISO/IEC 18004:2015 Information – Automatic identification and data capture techniques – QR Code barcode symbology specification. This renames the QR Code 2005 symbol to QR Code and adds clarification to some procedures and minor corrections.
The majority of implementations differ slightly at the application layer. NTT DoCoMo, a Japanese telecommunications company, has established de facto standards for the encoding of URLs, contact information, and a variety of other data types.
A list of QR code data types is maintained by the open-source “ZXing” project.
Use-cases
Analytics and campaign tracking
![]()
When conducting advertising campaigns a QR code can help capture analytical information for example a QR code could link to a shortened link which will record information when a visitor opens the link such as the country, state and device type used by the end-user.
This can help in the market analysis stage to break down visitors into different categories such as:
- Device type (Smartphone, tablet or computer) or Android/iOS
- Country and region
- Browser used e.g. Firefox, Chrome or Safari
Checking in and reservations

QR Code technology has been used by the Hospitality space and Medical clinics for many years and can be used for purposes such as making bookings/reservations or scheduling out appointments.
In addition to the above the use of QR code technology was adopted by many Governments throughout the COVID-19 pandemic as a means of identifying visitors to events and venues.
Wi-Fi network sharing

Many hotels and venues that offer free Wi-Fi to their visitors will often include the configuration in a QR code that can be scanned by a smartphone and easily connect to the network.
Bike, scooter and car sharing

In urban areas bike, car and scooter sharing is quite popular and QR technology is often used in the registration process for people to make payment and complete the rental of the vehicle.
Events shown on posters

Some posters for different events such as music festivals will often include a code to scan which will take visitors directly to a booking page where they can pay and make a booking for the event.
Links to more information

If you need to share a long URL to provide additional information then a QR code can be the perfect solution for this purpose.
Some examples where this is utilized include:
- Industry trade shows
- Food nutrition information
- Social media profiles to follow for updates
- Specific articles or blog posts
Example codes:
Here is some example QR codes that will take you to the AGR Technology Facebook and Twitter profiles.


Conclusion
We hope you found this resource page to be helpful and explain how the QR technology works. Be sure to share this with others who may be interested and find it to be useful.
Also check out our blog for more tips and follow AGR Technology for more updates by scanning the codes above.
Source(s) cited:
“QR code” Wikipedia, 16 July 2004, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/QR_code. Accessed 31 Jan. 2022.
Related content from our technology glossary:
![logo-new-23[1] logo-new-23[1]](https://agrtech.com.au/wp-content/uploads/elementor/thumbs/logo-new-231-qad2sqbr9f0wlvza81xod18hkirbk9apc0elfhpco4.png)