To get started simply click on the buttons “encode” and “decode” to open a drop-down where you can input your text.
Introduction

Base64 encoders and decoders translate data between binary and text formats, making them essential tools for developers and IT professionals. These utilities work in tandem to ensure data integrity during transmission across different systems.
This type of encoding is a crucial technique that converts binary data into a text format that can be safely transmitted across systems that only handle plain text. It’s widely used in web applications, email systems, and data storage where binary data needs to be embedded in text-based formats.
The technology is also widely used in many types of software to encode data and can be transferred whilst keeping the content intact. Some uses of Base64 include email over MIME and storing configuration in XML or JSON files. Our online tool is 100% free to use in your browser and won’t require you to download anything meaning it will work on any platform directly inside your favorite browser.
The encoding process transforms arbitrary sequences of octets into a string representation using a set of 64 characters as defined in RFC 4648. When decoding, these text strings are converted back to their original binary form. Base64 comes in two primary variations: the standard alphabet (using ‘+’ and ‘/’) and the URL-safe version (using ‘-‘ and ‘_’), each serving different use cases in modern computing.
While Base64 encoding increases data size by approximately 33%, it ensures compatibility across various systems and prevents data corruption during transmission, making it an essential tool in today’s interconnected digital landscape.
If you find this tool useful consider supporting our business on Paypal or checking out our YouTube channel and other software tools.
Why use our tool?
- 100% free to use with no downloads needed
- Securely rendered in your browser through SSL/TLS
- Quick and easy to use
How to encode & decode base64 text (video tutorial)
Example
Here is an example of text that has been encoded in Base64
Regular text:
the quick brown fox jumped over the lazy dog
Encoded version:
Technical background information about Base64
Base64 is a group of binary-to-text encoding schemes used in programming to represent binary data (specifically, a sequence of 8-bit bytes) in an ASCII string format by converting the data to a radix-64 representation. The term Base64 is derived from a particular MIME content transfer encoding. Each non-final Base64 digit corresponds to 6 bits of data.
Three 8-bit bytes (for a total of 24 bits) are thus represented by four 6-bit Base64 digits. Base64, like all binary-to-text encoding schemes, is intended to transport data stored in binary formats across channels that can only reliably support text content.
This is required because SMTP – in its original form – was designed to transport 7-bit ASCII characters only. This encoding causes an overhead of 33–36% (33% by the encoding itself; up to 3% more by the inserted line breaks). The particular set of 64 characters chosen to represent the 64-digit values for the base varies between implementations.
The general strategy is to choose 64 characters that are common to most encodings and that are also printable. This combination leaves the data unlikely to be modified in transit through information systems, such as email, that were traditionally not 8-bit clean.
For example, MIME’s Base64 implementation uses A–Z, a–z, and 0–9 for the first 62 values. Other variations share this property but differ in the symbols chosen for the last two values; an example is UTF-7. The earliest instances of this type of encoding were created for dial-up communication between systems running the same OS — e.g., uuencode for UNIX, BinHex for the TRS-80 (later adapted for the Macintosh) — and could therefore make more assumptions about what characters were safe to use. For instance, uuencode uses uppercase letters, digits, and many punctuation characters, but no lowercase.
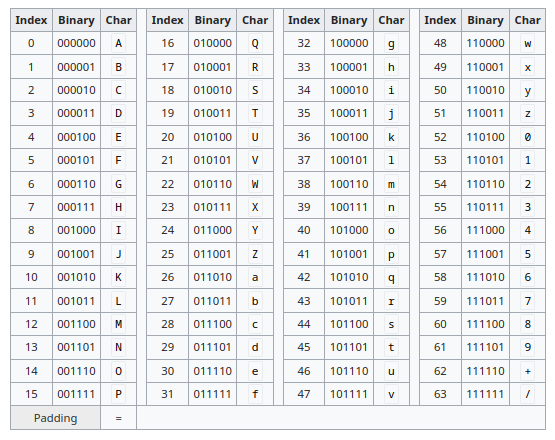
Base64 table:
Programming Libraries
Programming languages include native libraries that support Base64 operations, enabling developers to implement encoding and decoding functions directly in their applications.
| Language | Encoding Example | Decoding Example |
|---|---|---|
| JavaScript | btoa("Hello World") |
atob("SGVsbG8gV29ybGQ=") |
| Python | base64.b64encode(b"Hello World") |
base64.b64decode("SGVsbG8gV29ybGQ=") |
| PHP | base64_encode("Hello World") |
base64_decode("SGVsbG8gV29ybGQ=") |
| Java | Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString("Hello World".getBytes()) |
new String(Base64.getDecoder().decode("SGVsbG8gV29ybGQ=")) |
These libraries handle the complexities of padding, character sets, and error handling, making Base64 operations straightforward across development environments.
Key Takeaways
- Base64 encoding converts binary data into text format, increasing size by approximately 33% while ensuring safe transmission across text-only systems
- Two primary Base64 variations exist: standard alphabet (using ‘+’ and ‘/’) and URL-safe version (using ‘-‘ and ‘_’), each serving different application needs
- Online Base64 tools provide instant, cross-platform encoding/decoding capabilities without requiring software installation
- Command-line utilities for Base64 operations are built into Linux, macOS, and Windows PowerShell, making them ideal for scripting and automation
- Most programming languages offer native Base64 libraries, with JavaScript, Python, PHP, and Java all providing simple encoding and decoding functions
- The Base64 character set consists of 64 characters: uppercase A-Z, lowercase a-z, digits 0-9, and two special characters
Summary
Base64 encoding stands as a cornerstone technology in digital communication enabling the safe transmission of binary data across text-only systems. While it increases file size by approximately 33% this trade-off delivers crucial compatibility and data integrity benefits.
Today’s developers have numerous options for implementing Base64 from convenient online tools like Base64Decode.org to built-in command-line utilities across operating systems and robust programming libraries in JavaScript Python PHP and Java.
Whether you’re embedding images in HTML emails transmitting complex data structures or working with APIs understanding Base64 provides an essential skill for modern development work. Its simplicity reliability and universal adoption make it an indispensable tool in the digital toolkit.
Conclusion
We hope you found this tool to be helpful, if so please consider sharing it or following agrtech on social media. AGR Technology is an Australian business providing a range of solutions such as Software Development, Website Design and more to businesses of all sizes in Australia and abroad.Source(s) cited:
(2003). Base64 [Online]. Wikipedia. Available at: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Base64 (Accessed: 6 June 2021).
What is Base64 encoding?
Base64 encoding is a technique that converts binary data into text format using 64 characters. It transforms data into a representation that can be safely transmitted across systems that only support plain text. The standard encoding uses uppercase letters (A-Z), lowercase letters (a-z), numbers (0-9), and the symbols “+” and “/”, while URL-safe versions replace “+” and “/” with “-” and “_” to avoid URL encoding issues.
Why is Base64 encoding important?
Base64 encoding ensures data compatibility across various systems and prevents corruption during transmission. It’s crucial for transferring binary data through text-only channels like email systems and certain web applications. Despite increasing data size by approximately 33%, Base64 encoding maintains data integrity, making it essential for secure data exchange in many digital communication scenarios.
Where is Base64 commonly used?
Base64 encoding is widely used in web applications (for embedding images in CSS/HTML), email systems (for sending attachments), data storage (for binary data in JSON), and API communications. It’s also frequently employed in authentication systems, digital signatures, and when transmitting binary data through text-only protocols. Any situation requiring binary-to-text conversion likely uses Base64.
What’s the difference between standard and URL-safe Base64?
Standard Base64 uses the characters A-Z, a-z, 0-9, “+”, and “/” with “=” for padding. URL-safe Base64 replaces “+” with “-” and “/” with “_” because the original characters have special meanings in URLs and can cause encoding issues. The URL-safe version ensures Base64 strings can be safely included in URLs without requiring additional encoding or causing parsing problems.
Can I use command-line utilities for Base64 operations?
Yes, most operating systems have built-in command-line utilities for Base64 encoding and decoding. On Linux and macOS, use the base64 command. For Windows PowerShell, utilize [Convert]::ToBase64String() and [Convert]::FromBase64String() methods. These command-line tools are particularly useful for batch processing or incorporating Base64 operations into scripts and automated workflows.
Does Base64 encoding provide any security?
No, Base64 encoding is not an encryption method and provides no security. It’s simply a data formatting technique that transforms binary data to text format. The transformation is easily reversible using standard algorithms, making it unsuitable for protecting sensitive information. For security purposes, proper encryption methods should be used alongside or instead of Base64 encoding.
How do programming languages handle Base64 encoding?
Most programming languages offer built-in libraries or methods for Base64 operations. JavaScript uses btoa() and atob(), Python has the base64 module, PHP provides base64_encode() and base64_decode() functions, and Java includes the Base64 class. These implementations handle the encoding complexities like bit manipulation and padding, making it easy for developers to incorporate Base64 functionality.
![logo-new-23[1] logo-new-23[1]](https://agrtech.com.au/wp-content/uploads/elementor/thumbs/logo-new-231-qad2sqbr9f0wlvza81xod18hkirbk9apc0elfhpco4.png)