Introduction – What is a subdomain and what is it’s purpose?
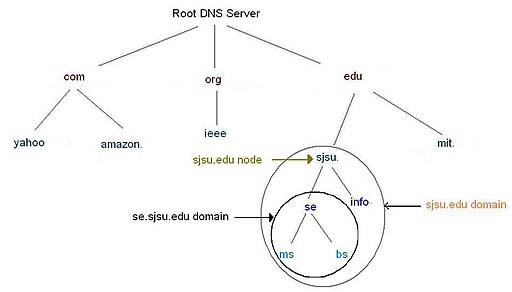
A sub domain is a domain that is part of another (main) domain in the Domain Name System (DNS) hierarchy. Subdomains are created by editing the DNS zone file for the parent domain. The term “subdomain” is often debated whether it should be used by system administrators when referring to names that map to the Address record A (host) and various other types of zone records.
Here’s an example of a subdomain on our website we created that shows new tweets we post to Twitter:
As you can see the “twitter” component of the URL is at the front but still attached to the root domain agrtech.com.au.
Subdomains allow websites to break down certain components and organize them in their own place without complicating the structure of the existing website. It can also facilitate the use of different frameworks, for example the root domain could be an informational page and a “Shop” subdomain could contain another website with eCommerce functionality.
Most web hosting services include the ability to add and remove subdomains on the server for the respective root domain as well as configure them to point to different locations.
Disadvantages & Advantages
Advantages:
- Provides options for scalability and distinguish content across a website
- Allows for a website to be better organized when large volumes of content are in place
- Provides options to mix technologies
Disadvantages:
- Potential SEO issues as the subdomain may be classed as a separate entity to the main website
- Requires extra work to maintain as each platform been used will have it’s own login and may require updates/patches to be installed.
- Can detract from the main website and make it harder for uses to find things especially if the URLs are long and complicated
Subdomains VS Sub-directories
A sub directory is different to a subdomain it that rather than been appended to the start of the root domain it sits underneath the main domain and is a part of the root.
An example of a sub-directory would be:
example.com/page1/
Both subdomains and sub-directories can be used to achieve the same thing however subdomains are generally better if a major part of a website needs to be differentiated from the main website.
A good example of this would be Google maps which is built on the main Google domain at: maps.google.com and functions independently to the search engine on the root domain.
Subdomains typically involve maintenance however as new software needs to be installed there and maintained with updates etc so in most cases sub-directories are far more convenient and easier to setup.
Use cases for subdomains
There are certain cases where subdomains are commonly used which include the following:
Translation & foreign language variations of content

For large websites that operate in multiple languages such as Wikipedia the different languages can be broken up to their own subdomains most commonly with the country code as the name for example:
en.wikipedia.org (English)
de.wikipedia.org (German)
ru.wikipedia.org (Russian)
es.wikipedia.org (Spanish/Español)
Organization of different departments
Organizations may choose to use subdomains in order to give a unique name to a department, function, or service. A university, for example, might assign “cs” to the computer science department. There are some well-known subdomains, such as WWW and FTP with WWW been for a public website and FTP for file access by admins. Access control over the domain’s various levels can be protected with independent authentication.
Staging test environments
Often times a web developer will setup a “staging” or “test” subdomain to test changes for a website without affecting the main website on the root domain.
This allows for new features to be deployed and to see how it will appear live without disrupting user sessions on the main website.
Mobile friendly versions of URL’s on a website

Using subdomains to create mobile friendly versions of URL’s is no longer a common practice like it once was with the rise of responsive web design which automatically renders the same web pages across different devices and screen sizes.
Prior to this however it was common practice for many websites to create subdomains such as “m” or “mobile” which had a copy of a page which was specifically designed for mobile often with less features then the desktop counterpart.
Here’s an example of multiple mobile subdomains used by Facebook at the time of writing:
Other large websites such as YouTube at the time of writing still have mobile subdomains left over from the time when smartphones and mobile computing was still in it’s early development.
Mixing different technologies
Subdomains can also be leveraged for complicated websites that require lots of different functionality for example a large website may have multiple sections such as a blog, forum and custom web application.
Using one large platform for the entire website might not be an option due to technical constraints or compatibility. In addition certain platforms are more specialized than others in specific areas.
For example a website like this may choose to have a “blog” subdomain running WordPress and then a “shop” subdomain using a platform like Shopify and then have the rest of the site written in pure HTML or in a specific language like the Microsoft ASP.NET framework.
This allows for each section of the website to be independent and take full advantage of the respective platform been used as well as allow for independent administration and hosting.
Implications for search engines
Whilst the use of subdomains has been controversial in the past within the Internet marketing field most people agree that subdomains are treated as semi-independent entities to the main root domain and as such typically won’t rank as well as a sub-directory which will benefit from SEO value to the main root domain more readily.
Most SEO consultants will often recommend only using subdomains if they make sense for a specific department for a large organization like a university or Government department.
As stated above subdomains are appropriate when there is a distinct part of a website which makes sense to break away from the main website due to it’s functionality.
Related links from our glossary:
Conclusion
We hope you found this page to be helpful, if so be sure to share it on social media and follow us on our social profiles to keep up with new content.
Also check out our free software/tools, business services, blog and video tutorials for more content.
Citations/References:
Wikimedia Foundation. (2021, May 14). Subdomain. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Subdomain.
Richard.bhuleskar at English Wikibooks, CC BY-SA 2.5 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.5, via Wikimedia Commons
![logo-new-23[1] logo-new-23[1]](https://cdn-ihdfn.nitrocdn.com/eZVJvoSTyVixkEUySRKiaseNtUlmgCyu/assets/images/optimized/rev-0174fc5/agrtech.com.au/wp-content/uploads/elementor/thumbs/logo-new-231-qad2sqbr9f0wlvza81xod18hkirbk9apc0elfhpco4.png)